Are There Any Ethnic Differences in the Response to Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- PMID: 34873553
- PMCID: PMC8636192
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20024
Are There Any Ethnic Differences in the Response to Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Abstract
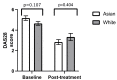
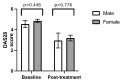
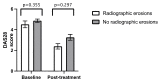
Introduction Baricitinib is an oral synthetic Janus Kinase inhibitor that inhibits JAK1 and JAK2, and the new kid on the block in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To date, there are no studies comparing the clinical benefit of baricitinib in RA between different ethnicities. Ethnicity plays a role in the effectiveness of therapeutic agents. Given the large multi-ethnic population of Leicestershire in the United Kingdom and the range of new therapeutics in RA, we reviewed our cohort of patients with RA to see whether there is any difference in baricitinib Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) response between the Asian and White cohorts. Methods This was a retrospective study. The patients included were those under the care of rheumatology at University Hospitals of Leicester (UHL) with a diagnosis of RA and either receiving baricitinib or had received it in the past. Data was collected using the UHL information technology systems, clinic letters and pharmacy records. In addition to ethnicity, we reviewed patient age, gender, concurrent disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) used, previous biologics used, baseline and post-treatment DAS28, dropout from therapy, baseline biochemical assays (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF) status) and radiographic findings. An independent t-test was used to compare continuous data, and Pearson's chi-squared test was used to compare categorical data. Results A total of 120 patients were included in the analysis, and data were analysed with Portable Format for Analytics (PFA). There was no statistically significant difference in the mean DAS28 at baseline (Asian: 5.17 versus White: 4.65; p-value = 0.107) and post-treatment (Asian: 2.8 versus White: 3.3; p-value = 0.404). Comparing both ethnicities, there was no statistically significant difference in previous biologics used, anti-CCP and RF titres, and radiographic findings of erosions. Conclusion This is the first study of its kind, and it found no significant difference in baricitinib response between the Asian and White cohorts. Our study had certain limitations, and future studies will be needed to evaluate this subject further. Such data is important as it can contribute to a body of evidence that may in the future help inform clinical decision-making.
Keywords: baricitinib; drug response; ethnicity; jak inhibitors; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021, Zahir Hussain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
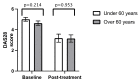

References
-
- Baricitinib versus placebo or adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Taylor PC, Keystone EC, van der Heijde D, et al. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:652–662. - PubMed
-
- Safety profile of baricitinib in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with over 2 years median time in treatment. Smolen JS, Genovese MC, Takeuchi T, et al. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Tailored first-line biologic therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Cantini F, Niccoli L, Nannini C, et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;45:519–532. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
