Research on the Mechanism of Guizhi to Treat Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
- PMID: 34873575
- PMCID: PMC8643239
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8141075
Research on the Mechanism of Guizhi to Treat Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
Abstract
Objective: Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is a common glomerular disease caused by a variety of causes and is the second most common kidney disease. Guizhi is the key drug of Wulingsan in the treatment of NS. However, the action mechanism remains unclear. In this study, network pharmacology and molecular docking were used to explore the underlying molecular mechanism of Guizhi in treating NS.
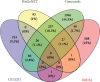
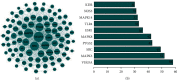
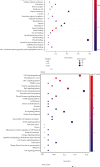
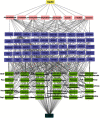
Methods: The active components and targets of Guizhi were screened by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP), Hitpick, SEA, and Swiss Target Prediction database. The targets related to NS were obtained from the DisGeNET, GeneCards, and OMIM database, and the intersected targets were obtained by Venny2.1.0. Then, active component-target network was constructed using Cytoscape software. And the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was drawn through the String database and Cytoscape software. Next, Gene Ontology (GO) and pathway enrichment analyses of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were performed by DAVID database. And overall network was constructed through Cytoscape. Finally, molecular docking was conducted using Autodock Vina.
Results: According to the screening criteria, a total of 8 active compounds and 317 potential targets of Guizhi were chosen. Through the online database, 2125 NS-related targets were identified, and 93 overlapping targets were obtained. In active component-target network, beta-sitosterol, sitosterol, cinnamaldehyde, and peroxyergosterol were the important active components. In PPI network, VEGFA, MAPK3, SRC, PTGS2, and MAPK8 were the core targets. GO and KEGG analyses showed that the main pathways of Guizhi in treating NS involved VEGF, Toll-like receptor, and MAPK signaling pathway. In molecular docking, the active compounds of Guizhi had good affinity with the core targets.
Conclusions: In this study, we preliminarily predicted the main active components, targets, and signaling pathways of Guizhi to treat NS, which could provide new ideas for further research on the protective mechanism and clinical application of Guizhi against NS.
Copyright © 2021 Dan He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Liuwei Dihuang Pills in Treating Parkinson's Disease Based on Network Pharmacology.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 28;2021:4490081. doi: 10.1155/2021/4490081. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34746302 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Validation to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanism of Zhuling Decoction against Nephrotic Syndrome.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(28):2244-2256. doi: 10.2174/0113816128305808240529115047. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38910482
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Huoxiang Zhengqi Oral Liquid Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Modulating Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels and TLR4/NF-κB p65 Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Feb 17;2023:6183551. doi: 10.1155/2023/6183551. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36845637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krishnan R. G. Nephrotic syndrome. Paediatrics and Child Health . 2012;22(8):337–340. doi: 10.1016/j.paed.2012.02.004. - DOI
-
- Shah S. S., Akhtar N., Sunbleen F., ur Rehman M. F., Ahmed T. Histopathological patterns in paediatric idiopathic steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad: JAMC . 2015;27(3):633–636. - PubMed
-
- Gao Y. X., Zhang P. Q., Zhang Q. Professor Zhang Qi's experience in treating refractory nephrotic syndrome edema with “tong”. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Nephrology . 2014;5(8):663–664.
-
- Zhang X. L., Liu C. H., Li H. J., Tian M., Wu L. J., Cao G. H. Effect of Guizhifuling Decoction combined with hormone on primary nephrotic syndrome in children and its effect on serum inflammatory factors. Shaanxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine . 2018;39(11):1609–1612.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

