Phylogenomics of two ST1 antibiotic-susceptible non-clinical Acinetobacter baumannii strains reveals multiple lineages and complex evolutionary history in global clone 1
- PMID: 34874246
- PMCID: PMC8767349
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000705
Phylogenomics of two ST1 antibiotic-susceptible non-clinical Acinetobacter baumannii strains reveals multiple lineages and complex evolutionary history in global clone 1
Abstract
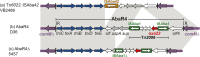
Acinetobacter baumannii is an opportunistic pathogen that is difficult to treat due to its resistance to extreme conditions, including desiccation and antibiotics. Most strains causing outbreaks around the world belong to two main global lineages, namely global clones 1 and 2 (GC1 and GC2). Here, we used a combination of Illumina short read and MinION (Oxford Nanopore) long-read sequence data with a hybrid assembly approach to complete the genome sequence of two antibiotic-sensitive GC1 strains, Ex003 and Ax270, recovered in Lebanon from water and a rectal swab of a cat, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis of Ax270 and Ex003 with 186 publicly available GC1 genomes revealed two major clades, including five main lineages (L1-L5), and four single-isolate lineages outside of the two clades. Ax270 and Ex003, along with AB307-0294 and MRSN7213 (both predicted antibiotic-susceptible isolates) represent these individual lineages. Antibiotic resistance islands and transposons interrupting the comM gene remain important features in L1-L5, with L1 associated with the AbaR-type resistance islands, L2 with AbaR4, L3 strains containing either AbaR4 or its variants as well as Tn6022::ISAba42, and L4 and L5 associated with Tn6022 or its variants. Analysis of the capsule (KL) and outer core (OCL) polysaccharide loci further revealed a complex evolutionary history probably involving many recombination events. As more genomes become available, more GC1 lineages continue to emerge. However, genome sequence data from more diverse geographical regions are needed to draw a more accurate population structure of this globally distributed clone.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; GC1; ST1; antibiotic resistance; global clone; whole genome sequence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

