Correlation between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma neurofilament light protein in treated HIV infection: results from the COBRA study
- PMID: 34874540
- PMCID: PMC9076742
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-021-01026-3
Correlation between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma neurofilament light protein in treated HIV infection: results from the COBRA study
Abstract
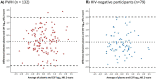
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) neurofilament light protein (NfL) is a marker of central nervous system neuro-axonal injury. A novel, ultra-sensitive assay can determine plasma NfL. In untreated people-with-HIV (PWH), CSF and plasma NfL are strongly correlated. We aimed to assess this correlation in PWH on suppressive antiretroviral treatment (ART) and lifestyle-similar HIV-negative individuals enrolled into the COmorBidity in Relation to AIDS (COBRA) study. Differences in paired CSF (sandwich ELISA, UmanDiagnostics) and plasma (Simoa digital immunoassay, Quanterix™) NfL between PWH and HIV-negative participants were tested using Wilcoxon's test; associations were assessed using Pearson's correlation. CSF and plasma NfL, standardised to Z-scores, were included as dependent variables in linear regression models to identify factors independently associated with values in PWH and HIV-negative participants. Overall, 132 PWH (all with plasma HIV RNA < 50 copies/mL) and 79 HIV-negative participants were included. Neither CSF (median 570 vs 568 pg/mL, p = 0.37) nor plasma (median 10.7 vs 9.9 pg/mL, p = 0.15) NfL differed significantly between PWH and HIV-negative participants, respectively. CSF and plasma NfL correlated moderately, with no significant difference by HIV status (PWH: rho = 0.52; HIV-negative participants: rho = 0.47, p (interaction) = 0.63). In multivariable regression analysis, higher CSF NfL Z-score was statistically significantly associated with older age and higher CSF protein, and higher plasma NfL Z-score with older age, higher serum creatinine and lower bodyweight. In conclusion, in PWH on ART, the correlation between CSF and plasma NfL is moderate and similar to that observed in lifestyle-similar HIV-negative individuals. Consideration of renal function and bodyweight may be required when utilising plasma NfL.
Keywords: Axons; Central nervous system diseases; HIV; HIV-1; Neurofilament proteins.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JA has received financial support to attend scientific conferences from MSD, Janssen UK and Gilead Sciences. HZ has served on scientific advisory boards for Denali, Roche Diagnostics, Wave, Samumed and CogRx; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Ventures-based platform company at the University of Gothenburg (outside submitted work). JU has received honoraria for preparation of educational materials and has served on an advisory board for Gilead Sciences. MG has received research grants from Gilead Sciences and Janssen-Cilag and honoraria as speaker and/or scientific advisor from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline/ViiV, Janssen-Cilag and MSD. PR through his institution has received independent scientific grant support from Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc., Merck & Co and ViiV Healthcare, and has served on scientific advisory boards for Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, Merck & Co. and Teva pharmaceutical industries, for which honoraria were all paid to his institution. AW has received honoraria or research grants on behalf of Imperial College London or been a consultant or investigator in clinical trials sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen-Cilag, Roche and ViiV Healthcare. CAS has received funding for the membership of Data Safety and Monitoring Boards, Advisory Boards and for preparation of educational materials from Gilead Sciences and ViiV Healthcare. For the remaining authors, none were declared.
Figures
References
-
- Booiman T, Wit FW, Girigorie AF, Maurer I, De Francesco D, Sabin CA, Harskamp AM, Prins M, Franceschi C, Deeks SG, Winston A, Reiss P, Kootstra NA. Terminal differentiation of T cells is strongly associated with CMV infection and increased in HIV-positive individuals on ART and lifestyle matched controls. PLoS ONE. 2017 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183357. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bridel C, Van Wieringen WN, Zetterberg H, Tijms BM, Teunissen CE, Alvarez-Cermeño JC, Andreasson U, Axelsson M, Bäckström DC, Bartos A, Bjerke M, Blennow K, Boxer A, Brundin L, Burman J, Christensen T, Fialová L, Forsgren L, Frederiksen JL, Wild EJ. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019 doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Francesco D, Wit FW, Cole JH, Kootstra NA, Winston A, Sabin CA, Underwood J, Van Zoest RA, Schouten J, Kooij KW, Prins M, Guaraldi G, Caan MWA, Burger D, Franceschi C, Libert C, Bü Rkle A, Reiss P. The “COmorBidity in Relation to AIDS” (COBRA) cohort: Design, methods and participant characteristics, on behalf of the COmorBidity in Relation to AIDS (COBRA) collaboration. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(3):e0191791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191791. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical