Gene expression profiling reveals the genomic changes caused by MLN4924 and the sensitizing effects of NAPEPLD knockdown in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 34874801
- PMCID: PMC8837228
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2014254
Gene expression profiling reveals the genomic changes caused by MLN4924 and the sensitizing effects of NAPEPLD knockdown in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
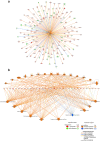
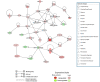
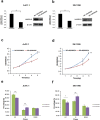
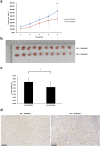
MLN4924 inhibits the proteolytic degradation of Cullin-Ring E3 ligase (CRL) substrates and exhibits antitumor activity toward various malignancies, including pancreatic cancer. MLN4924 suppresses tumor growth by altering various key regulator proteins; however, its impact on gene expression in tumors remains unknown. In this study, the genomic changes caused by MLN4924 in pancreatic cancer were examined by gene chip analysis and ingenuity pathway analysis. Eleven pathways were significantly altered (5 activated and 6 inhibited), 45 functions were significantly changed (21 activated and 24 inhibited), and the most activated upstream factor was predicted to be TNF. Of 691 differentially expressed genes, NAPEPLD knockdown showed synergism with MLN4924, as determined by real-time quantitative PCR and high content screening. NAPEPLD knockdown enhanced the effect of MLN4924 on inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in vitro. In a pancreatic cancer nude mouse model, MLN4924 inhibited tumor growth more significantly in the NAPEPLD knockdown group than in the control group. NAPEPLD expression was higher in pancreatic cancer tissues than in the normal pancreas but was not associated with prognosis. These findings indicate that MLN4924 causes extensive genomic changes in pancreatic cancer cells, and targeting NAPEPLD may increase the efficacy of MLN4924.
Keywords: Pancreatic neoplasms; genetic profile; high-throughput screening assays; molecular targeted therapy; proteasome inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Mizrahi JD, Surana R, Valle JW, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2020;395(10242):2008–2020. - PubMed
-
- Hackert T, Klaiber U, Pausch T, et al. Fifty Years of Surgery for Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas. 2020;49(8):1005–1013. - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus Gemcitabine for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1817–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
