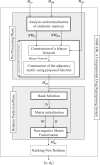
A network-based drug repurposing method via non-negative matrix factorization
- PMID: 34875000
- PMCID: PMC8825773
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab826
A network-based drug repurposing method via non-negative matrix factorization
Abstract
Motivation: Drug repurposing is a potential alternative to the traditional drug discovery process. Drug repurposing can be formulated as a recommender system that recommends novel indications for available drugs based on known drug-disease associations. This article presents a method based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF-DR) to predict the drug-related candidate disease indications. This work proposes a recommender system-based method for drug repurposing to predict novel drug indications by integrating drug and diseases related data sources. For this purpose, this framework first integrates two types of disease similarities, the associations between drugs and diseases, and the various similarities between drugs from different views to make a heterogeneous drug-disease interaction network. Then, an improved non-negative matrix factorization-based method is proposed to complete the drug-disease adjacency matrix with predicted scores for unknown drug-disease pairs.
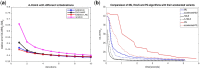
Results: The comprehensive experimental results show that NMF-DR achieves superior prediction performance when compared with several existing methods for drug-disease association prediction.
Availability and implementation: The program is available at https://github.com/sshaghayeghs/NMF-DR.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Atif S.M. et al. (2019) Improved svd-based initialization for nonnegative matrix factorization using low-rank correction. Pattern Recogn. Lett., 122, 53–59.
-
- Berry M.W. et al. (2007) Algorithms and applications for approximate nonnegative matrix factorization. Comput. Stat. Data Anal., 52, 155–173.
-
- Bokde D. et al. (2015) Matrix factorization model in collaborative filtering algorithms: a survey. Procedia Comput. Sci., 49, 136–146.
-
- Ceddia G. et al. (2019) Non-negative matrix tri-factorization for data integration and network-based drug repositioning. In: 2019 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), IEEE, Siena, Italy. pp. 1–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources