Long-term follow-up after lymphodepleting autologous haematopoietic cell transplantation for treatment-resistant systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 34875023
- PMCID: PMC9348613
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab877
Long-term follow-up after lymphodepleting autologous haematopoietic cell transplantation for treatment-resistant systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: Autologous haematopoietic cell transplantation (AHSCT) improves immunologic dysfunction in patients with SLE. However, the curative potential of this therapy remains uncertain. This study reports outcomes in SLE patients receiving a lymphodepleting, reduced intensity regimen for AHSCT in SLE.
Methods: Eight patients with SLE refractory to treatment, including i.v. cyclophosphamide (CYC), were enrolled. Five had LN and three CNS involvement as primary indications for transplant. Haematopoietic cell mobilization with CYC, G-CSF and rituximab was followed by collection of CD34+ positively selected cells. The conditioning regimen consisted of concurrent administration of CYC, fludarabine and rituximab. All immunosuppressive medications were discontinued at the start of mobilization and CS were rapidly tapered after the transplant.
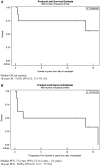
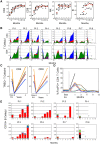
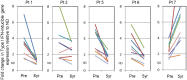
Results: Five of eight patients achieved a complete response, including a decline in the SLEDAI to zero, which was sustained in four patients for a median of 165 months (range 138-191). One patient achieved a partial response, which was followed by relapse at month 18. Two patients with nephritis and underlying comorbidities in most organs had early deaths from infection and multiorgan failure. AHSCT resulted in profound lymphodepletion, followed by expansion of Treg cells and repopulation of naive T and B cells. Patients with a complete response showed a sustained suppression of the SLE-associated IFN-induced gene signature, marked depletion of memory and plasmablast B cells and resultant sustained elimination of anti-dsDNA antibody.
Conclusion: Durable clinical and serologic remissions with suppression in the IFN gene signature can be achieved in refractory SLE following lymphodepleting AHSCT.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, https://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT00076752.
Keywords: SLE; cytokine; interferon; lymphodepletion; stem cell transplantation.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology 2021. This work is written by a US Government employee and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term follow-up of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for refractory lupus nephritis-a series study of 20 patients.Lupus. 2022 Nov;31(13):1586-1594. doi: 10.1177/09612033221126848. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Lupus. 2022. PMID: 36117428
-
Nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus.JAMA. 2006 Feb 1;295(5):527-35. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.5.527. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 16449618 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined transplantation of autologous hematopoietic stem cells and allogenic mesenchymal stem cells increases T regulatory cells in systemic lupus erythematosus with refractory lupus nephritis and leukopenia.Lupus. 2015 Oct;24(11):1221-6. doi: 10.1177/0961203315583541. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Lupus. 2015. PMID: 25914407
-
Immune ablation with stem-cell rescue: a possible cure for systemic lupus erythematosus?Lupus. 1993 Jun;2(3):151-6. doi: 10.1177/096120339300200304. Lupus. 1993. PMID: 8103697 Review.
-
Health-related quality of life in systemic sclerosis before and after autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplant-a systematic review.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Apr 1;59(4):779-789. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez300. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 31504944
Cited by
-
The essential roles of memory B cells in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Dec;20(12):770-782. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01179-5. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39511302 Review.
-
Sequential immunotherapy: towards cures for autoimmunity.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Jul;23(7):501-524. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00959-8. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38839912 Review.
-
Defining immune reset: achieving sustained remission in autoimmune diseases.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Jul;25(7):528-541. doi: 10.1038/s41577-025-01141-w. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40044810 Review.
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Autoimmune Neurological Diseases: An Update.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;10(2):176. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020176. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus: updated insights on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and therapeutics.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 17;10(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02168-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40097390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lateef A, Petri M.. Biologics in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2010;22:504–9. - PubMed
-
- Alexander T, Thiel A, Rosen O. et al. Depletion of autoreactive immunologic memory followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with refractory SLE induces long-term remission through de novo generation of a juvenile and tolerant immune system. Blood 2009;113:214–23. - PubMed

