Association of diabetes with atrial fibrillation types: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34876114
- PMCID: PMC8653594
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01423-2
Association of diabetes with atrial fibrillation types: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common arrhythmia classified as paroxysmal and non-paroxysmal. Non-paroxysmal AF is associated with an increased risk of complications. Diabetes contributes to AF initiation, yet its role in AF maintenance is unclear. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to summarize the evidence regarding the association of diabetes with AF types.
Methods: We searched 5 databases for observational studies investigating the association of diabetes with the likelihood of an AF type (vs another type) in humans. Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Studies classifying AF types as paroxysmal (reference) and non-paroxysmal were pooled in a meta-analysis using random effects models.
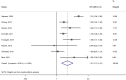
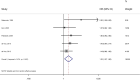
Results: Of 1997 articles we identified, 20 were included in our systematic review. The population sample size ranged from 64 to 9816 participants with mean age ranging from 40 to 75 years and percentage of women from 24.8 to 100%. The quality of studies varied from poor (60%) to fair (5%) to good (35%). In the systematic review, 8 studies among patients with AF investigated the cross-sectional association of diabetes with non-paroxysmal AF (vs paroxysmal) of which 6 showed a positive association and 2 showed no association. Fourteen studies investigated the longitudinal association of diabetes with "more sustained" AF types (vs "less sustained") of which 2 showed a positive association and 12 showed no association. In the meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies, patients with AF and diabetes were 1.31-times more likely to have non-paroxysmal AF than those without diabetes [8 studies; pooled OR (95% CI), 1.31 (1.13-1.51), I2 = 82.6%]. The meta-analysis of longitudinal studies showed that for patients with paroxysmal AF, diabetes is associated with 1.32-times increased likelihood of progression to non-paroxysmal AF [five studies; pooled OR (95% CI), 1.32 (1.07-1.62); I2 = 0%].
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that diabetes is associated with an increased likelihood of non-paroxysmal AF rather than paroxysmal AF. However, further high quality studies are needed to replicate these findings, adjust for potential confounders, elucidate mechanisms linking diabetes to non-paroxysmal AF, and assess the impact of antidiabetic medications on AF types. These strategies could eventually help decrease the risk of non-paroxysmal AF among patients with diabetes.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Diabetes mellitus; Non-paroxysmal; Paroxysmal; Permanent; Persistent.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and predictors of atrial fibrillation progression: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heart Rhythm. 2019 Apr;16(4):502-510. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Heart Rhythm. 2019. PMID: 30366160
-
Distribution and risk profile of paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent atrial fibrillation in routine clinical practice: insight from the real-life global survey evaluating patients with atrial fibrillation international registry.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012 Aug 1;5(4):632-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.112.970749. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22787011
-
Associations between adipokines and atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022 Apr;32(4):853-862. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.01.019. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35227548
-
Relationship between diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation prevalence in the Polish population: a report from the Non-invasive Monitoring for Early Detection of Atrial Fibrillation (NOMED-AF) prospective cross-sectional observational study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Jun 24;20(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01318-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34167520 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperuricemia is associated with an increased prevalence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes referred for clinically indicated 24-h Holter monitoring.J Endocrinol Invest. 2018 Feb;41(2):223-231. doi: 10.1007/s40618-017-0729-4. Epub 2017 Jul 15. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018. PMID: 28711969
Cited by
-
The Cardiac-Kidney-Liver (CKL) syndrome: the "real entity" of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Med Sci. 2024 Jan 31;20(1):207-215. doi: 10.5114/aoms/183070. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38414467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of atrial fibrillation on a 24-hour Holter in adult Indians.Indian Heart J. 2024 May-Jun;76(3):218-220. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2024.06.012. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Indian Heart J. 2024. PMID: 38878964 Free PMC article.
-
The Synergistic Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health.Cureus. 2023 Sep 24;15(9):e45881. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45881. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37885547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation Burden and Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Bidirectional Relationship.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Jun;121(6):e20230680. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230680. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39016411 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Glycemic control and atrial fibrillation: an intricate relationship, yet under investigation.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Mar 14;21(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01473-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35287684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983–988. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98(10):946–952. - PubMed
-
- Kim MH, Johnston SS, Chu BC, Dalal MR, Schulman KL. Estimation of total incremental health care costs in patients with atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2011;4(3):313–320. - PubMed
-
- Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2010;31(19):2369–2429. - PubMed

