MiR-155-5p suppresses SOX1 to promote proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma via RAF/MEK/ERK pathway
- PMID: 34876142
- PMCID: PMC8650398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02374-0
MiR-155-5p suppresses SOX1 to promote proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma via RAF/MEK/ERK pathway
Abstract
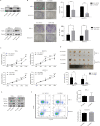
Background: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated the close relation of SOX1 with tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Upregulation of SOX1 was recently shown to suppress growth of human cancers. However, the expression and role of SOX1 in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is not well characterized.
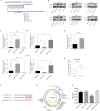
Methods: Expression levels of SOX1 in CCA tissues and normal bile duct tissues were examined using public GEO database. Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to confirm the expression levels. Cell proliferation assay (CCK-8) and colony formation assay were performed to assess proliferation of CCA cells. A mouse model of subcutaneous transplantable tumors was used to evaluated proliferation of CCA in vivo. The putative regulating factor of SOX1 were determined using Targetscan and dual-luciferase reporter assay.
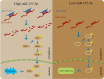
Results: SOX1 was downregulated in CCA tissues. Overexpression of SOX1 significantly inhibited cell proliferation in vitro and suppressed tumor growth in vivo. miR-155-5p directly targeted the 3'-untranslated region (3'UTR) of SOX1 and inhibited expression of SOX1, resulting in the activation of RAF, MEK and ERK phosphorylation, and thus CCA proliferation. However, restoration of SOX1 expression in miR-155-5p overexpressing cell lines decreased the phosphorylation level of RAF, MEK and ERK, as well as the proliferation of CCA cells.
Conclusion: MiR-155-5p decreased the expression of SOX1 by binding to its 3'UTR, which activated the RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and promoted CCA progression.
Keywords: Cholangiocarcinoma; ERK; RAF; SOX1; miRNA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

