Device-measured physical activity, adiposity and mortality: a harmonised meta-analysis of eight prospective cohort studies
- PMID: 34876405
- PMCID: PMC9209690
- DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2021-104827
Device-measured physical activity, adiposity and mortality: a harmonised meta-analysis of eight prospective cohort studies
Abstract
Background: The joint associations of total and intensity-specific physical activity with obesity in relation to all-cause mortality risk are unclear.
Methods: We included 34 492 adults (72% women, median age 62.1 years, 2034 deaths during follow-up) in a harmonised meta-analysis of eight population-based prospective cohort studies with mean follow-up ranging from 6.0 to 14.5 years. Standard body mass index categories were cross-classified with sample tertiles of device-measured total, light-to-vigorous and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and sedentary time. In five cohorts with waist circumference available, high and low waist circumference was combined with tertiles of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity.
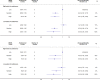
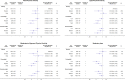
Results: There was an inverse dose-response relationship between higher levels of total and intensity-specific physical activity and mortality risk in those who were normal weight and overweight. In individuals with obesity, the inverse dose-response relationship was only observed for total physical activity. Similarly, lower levels of sedentary time were associated with lower mortality risk in normal weight and overweight individuals but there was no association between sedentary time and risk of mortality in those who were obese. Compared with the obese-low total physical activity reference, the HRs were 0.59 (95% CI 0.44 to 0.79) for normal weight-high total activity and 0.67 (95% CI 0.48 to 0.94) for obese-high total activity. In contrast, normal weight-low total physical activity was associated with a higher risk of mortality compared with the obese-low total physical activity reference (1.28; 95% CI 0.99 to 1.67).
Conclusions: Higher levels of physical activity were associated with lower risk of mortality irrespective of weight status. Compared with obesity-low physical activity, there was no survival benefit of being normal weight if physical activity levels were low.
Keywords: body mass index; exercise; observational study.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) . Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017;390:2627–42. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration (BMI Mediated Effects), Lu Y, Hajifathalian K, et al. Metabolic mediators of the effects of body-mass index, overweight, and obesity on coronary heart disease and stroke: a pooled analysis of 97 prospective cohorts with 1·8 million participants. Lancet 2014;383:970–83. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61836-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
