Oncogenic microRNA-181d binding to OGT contributes to resistance of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin
- PMID: 34876558
- PMCID: PMC8651739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00715-6
Oncogenic microRNA-181d binding to OGT contributes to resistance of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin
Abstract
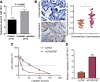
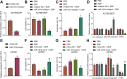
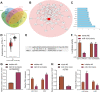
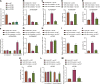
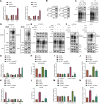
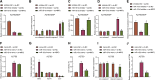
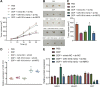
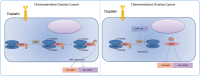
Ovarian cancer (OC), a common gynecological cancer, is characterized by a high malignant potential. MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) have been associated with the chemo- or radiotherapeutic resistance of human malignancies. Herein, the current study set out to explore the regulatory mechanism of miR-181d involved in the cisplatin (DDP) resistance of OC cells. Firstly, in-situ hybridization method was performed to identify miR-181d expression in ovarian tissues of DDP-resistant or DDP-sensitive patients. In addition, miR-181d expression in A2780 cells and A2780/DDP cell lines was determined by RT-qPCR. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments were then performed to characterize the effect of miR-181d on OC cell behaviors. We probed the miR-181d affinity to OGT, as well as the downstream glycosylation of KEAP1 and ubiquitination of NRF2. Further, in vivo experiments were performed to define the role of miR-181d in tumor resistance to DDP. miR-181d was highly expressed in the ovarian tissues of DDP-resistant patients and the A2780/DDP cell line. Ectopic expression of miR-181d augmented DDP resistance in OC cells. In addition, miR-181d was found to target the 3'UTR of OGT mRNA, and negatively regulate the OGT expression. Mechanistic results indicated that OGT repressed NRF2 expression through glycosylation of KEAP1, thereby inhibiting the DDP resistance of OC cells. Furthermore, miR-181d negatively orchestrated the OGT/KEAP1/NRF2 axis to enhance the OC resistance to DDP in vivo. Overall, these findings suggest that miR-181d-mediated OGT inhibition restricts the glycosylation of KEAP1, and then reduces the ubiquitination and degradation of NRF2, leading to DDP resistance of OC. This study provides new insights for prevention and control of OC.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

