Metabolism of tissue macrophages in homeostasis and pathology
- PMID: 34876704
- PMCID: PMC8891297
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00791-9
Metabolism of tissue macrophages in homeostasis and pathology
Abstract
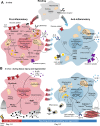
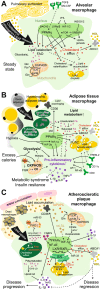
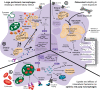
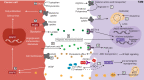
Cellular metabolism orchestrates the intricate use of tissue fuels for catabolism and anabolism to generate cellular energy and structural components. The emerging field of immunometabolism highlights the importance of cellular metabolism for the maintenance and activities of immune cells. Macrophages are embryo- or adult bone marrow-derived leukocytes that are key for healthy tissue homeostasis but can also contribute to pathologies such as metabolic syndrome, atherosclerosis, fibrosis or cancer. Macrophage metabolism has largely been studied in vitro. However, different organs contain diverse macrophage populations that specialize in distinct and often tissue-specific functions. This context specificity creates diverging metabolic challenges for tissue macrophage populations to fulfill their homeostatic roles in their particular microenvironment and conditions their response in pathological conditions. Here, we outline current knowledge on the metabolic requirements and adaptations of macrophages located in tissues during homeostasis and selected diseases.
Keywords: Tissue macrophages; homeostasis; metabolism; pathology; tissue regeneration.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ERC-2016-Consolidator Grant 725091/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- B2017/BMD-3733 Immunothercan-CM/Comunidad de Madrid
- 201723/Fundació la Marató de TV3 (TV3 Marathon Foundation)
- Retaining Junior Leader/"la Caixa" Foundation (Caixa Foundation)
- LCF/BQ/IN17/11620074/"la Caixa" Foundation (Caixa Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

