Cytological Effects of Serum Isolated from Polytraumatized Patients on Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 34876907
- PMCID: PMC8645412
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2612480
Cytological Effects of Serum Isolated from Polytraumatized Patients on Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
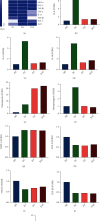
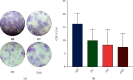
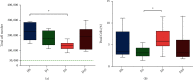
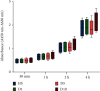
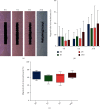
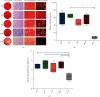
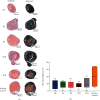
Due to their immunomodulatory and regenerative capacity, human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) are promising in the treatment of patients suffering from polytrauma. However, few studies look at the effects of sera from polytraumatized patients on hBMSCs. The aim of this study was to explore changes in hBMSC properties in response to serum from polytrauma patients taken at different time points after the trauma incident. For this, sera from 84 patients with polytrauma (collected between 2010 and 2020 in our department) were used. In order to test the differential influence on hBMSC, sera from the 1st (D1), 5th (D5), and 10th day (D10) after polytrauma were pooled, respectively. As a control, sera from three healthy donors (HS), matched with respect to age and gender to the polytrauma group, were collected. Furthermore, hBMSCs from four healthy donors were used in the experiments. The pooled sera of HS, D1, D5, and D10 were analyzed by multicytokine array for pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, the influence of the different sera on hBMSCs with respect to cell proliferation, colony forming unit-fibroblast (CFU-F) assay, cell viability, cytotoxicity, cell migration, and osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation was analyzed. The results showed that D5 serum significantly reduced hBMSC cell proliferation capacity compared with HS and increased the proportion of dead cells compared with D1. However, the frequency of CFU-F was not reduced in polytrauma groups compared with HS, as well as the other parameters. The serological effect of polytrauma on hBMSCs was related to the time after trauma. It is disadvantageous to use BMSCs in polytraumatized patients at least until the fifth day after polytrauma as obvious cytological changes could be found at that time point. However, it is promising to use hBMSCs to treat polytrauma after five days, combined with the concept of "Damage Control Orthopedics" (DCO).
Copyright © 2021 Yazhou Long et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Unfallchirurgie D. G. F. Definition of polytrauma. 2020, https://www.dgu-online.de/patienten/haeufige-diagnosen/schwerverletzte/p....
-
- Frenzel S., Krenn P., Heinz T., Negrin L. L. Does the applied polytrauma definition notably influence outcome and patient population? - a retrospective analysis. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine . 2017;25(1):87–87. doi: 10.1186/s13049-017-0400-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker S. P., O'Neill B. The injury severity score: an update. The Journal of Trauma . 1976;16(11):882–885. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

