Combined Metabolomics and Network Toxicology to Explore the Molecular Mechanism of Phytolacca acinose Roxb-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae in Vivo
- PMID: 34876912
- PMCID: PMC8645354
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3303014
Combined Metabolomics and Network Toxicology to Explore the Molecular Mechanism of Phytolacca acinose Roxb-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae in Vivo
Abstract
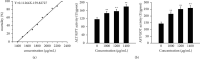
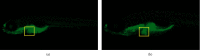
Phytolacca acinosa Roxb (PAR), a traditional Chinese medicine, has been widely used as a diuretic drug for a long period of time for the treatment edema, swelling, and sores. However, it has been reported that PAR might induce hepatotoxicity, while the mechanisms of its toxic effect are still unclear. In this study, network toxicology and metabolomic technique were applied to explore PAR-induced hepatotoxicity on zebrafish larvae. We evaluated the effect of PAR on the ultrastructure and the function of the liver, predictive targets, and pathways in network toxicology, apoptosis of liver cells by PCR and western blot, and metabolic profile by GC-MS. PAR causes liver injury, abnormal liver function, and apoptosis in zebrafish. The level of arachidonic acid in endogenous metabolites treated with PAR was significantly increased, leading to oxidative stress in vivo. Excessive ROS further activated the p53 signal pathway and caspase family, which were obtained from KEGG enrichment analysis of network toxicology. The gene levels of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 were significantly increased by RT-PCR, and the level of Caps3 protein was also significantly up-regulated through western blot. PAR exposure results in the liver function abnormal amino acid metabolism disturbance and motivates hepatocyte apoptosis, furthermore leading to liver injury.
Copyright © 2021 Dan Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial and financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hepatotoxicity of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb mediated by phytolaccagenin via ferroptosis/PPAR/P53/arachidonic acid metabolism.Phytomedicine. 2025 Mar;138:156433. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156433. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39892312
-
Integrating non-targeted metabolomics and toxicology networks to study the mechanism of Esculentoside A-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Jun;35(6):1-15. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22761. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33788351
-
Mechanistic insights into xanthomicrol as the active anti-HCC ingredient of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.: A network pharmacology analysis and transcriptomics integrated experimental verification.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 28;333:118467. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118467. Epub 2024 Jun 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38909826
-
Integrated spatially resolved metabolomics and network toxicology to investigate the hepatotoxicity mechanisms of component D of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115630. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115630. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35987407
-
Hepatotoxicity evaluation of Euphorbia kansui on zebrafish larvae in vivo.Phytomedicine. 2019 Sep;62:152959. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152959. Epub 2019 May 15. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31132752
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology: a crucial approach in traditional Chinese medicine research.Chin Med. 2025 Jan 12;20(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01056-z. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 39800680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gao H. M., Liu J. X., Wang Z. M., Wang W. H. Phytolacacinoside A, a new triterpenoid saponin from Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research . 2009;11(5):433–438. - PubMed
-
- Yifei Li G. Y. Review on pharmacological effects and toxicity of Phytolaccae. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae . 2020;17(13):248–251.
-
- Chen J. Clinical analysis on 26 cases of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine in treating aeate Phytolacca acinosa poisoning. Journal of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine . 2019;34(2):p. 221.
-
- Qian Zhou G. Y., Jin R., Xie J. Study on renal cell toxicity induced by esculentoside A. World Chinese Medicine . 2020;9(2):151–154.
-
- Qian Zhang G. Y., Jin R., Cui G. Preliminary Study on the Liver and Kidney Toxicity of Esculentoside A . Beijing, China: China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House; 2021. p. p. 223.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

