Intelligent Internet of Things Medical Technology in Implantable Intravenous Infusion Port in Children with Malignant Tumors
- PMID: 34876968
- PMCID: PMC8645386
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8936820
Intelligent Internet of Things Medical Technology in Implantable Intravenous Infusion Port in Children with Malignant Tumors
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Intelligent Internet of Things Medical Technology in Implantable Intravenous Infusion Port in Children with Malignant Tumors.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 18;2023:9806870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9806870. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37886336 Free PMC article.
Abstract
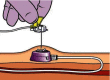
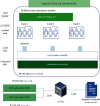
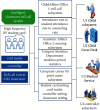
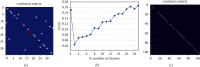
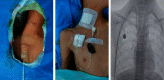
Due to the recent technological revolution that is centered around information technology, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has become an important research domain. IoMT is a combination of Internet of Things (IoT), big data, cloud computing, ubiquitous network, and three-dimensional holographic technology, which is used to build a smart medical diagnosis and treatment system. Additionally, this system should automate various activities, such as the patient's health record and health monitoring, which is an important issue in the development of modern and smart healthcare system. In this paper, we have thoroughly examined the role of a smart healthcare system architecture and other key supporting technologies in improving the health status of both indoor and outdoor patients. The proposed system has the capacity to investigate and predict (if feasible) the clinical application and nursing effects of totally implantable intravenous port (TIVAP) in pediatric hematological tumors. For this purpose, seventy children with hematologic tumors were treated with TIVAP, and IoMT-enabled care was provided to them, where the occurrence of adverse events, specifically after the treatment, was observed. The experimental results collected after the 70 children were treated and cared for by TIVAP show that there were five cases of adverse events, whereas the incidence rate of the adverse events was 7.14%. Moreover, TIVAP has significant efficacy in the treatment of hematologic tumors in children, and it equally reduces the vascular injury caused by chemotherapy in younger patients. Likewise, targeted care reduces the incidence of adverse events in children with expected ratio.
Copyright © 2021 Shaohong Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Toward the Internet of Medical Things: Architecture, trends and challenges.Math Biosci Eng. 2024 Jan;21(1):650-678. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2024028. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Math Biosci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38303438 Review.
-
AI-Enabled Framework for Fog Computing Driven E-Healthcare Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;21(23):8039. doi: 10.3390/s21238039. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34884048 Free PMC article.
-
An Intelligent Collection System of Big Data in Medical and Health Education Based on the Internet of Things.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 9;2022:3735102. doi: 10.1155/2022/3735102. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9852834. doi: 10.1155/2023/9852834. PMID: 35437463 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Intelligent Healthcare: Integration of Emerging Technologies and Internet of Things for Humanity.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 22;23(9):4200. doi: 10.3390/s23094200. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Survey of Authentication in Internet of Things-Enabled Healthcare Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;22(23):9089. doi: 10.3390/s22239089. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501799 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Intelligent Internet of Things Medical Technology in Implantable Intravenous Infusion Port in Children with Malignant Tumors.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 18;2023:9806870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9806870. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37886336 Free PMC article.
-
Design research on a smart infusion device to reduce medical workload and enhance patient safety.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 18;15(1):9265. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93911-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40102524 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of the combination of propofol and S(+)-ketamine for procedural sedation in pediatric patients undergoing totally implantable venous access port implantation: A prospective randomized controlled study.Front Pediatr. 2022 Aug 17;10:974917. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.974917. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36061400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartkamp A., Van Boxtel A. J. H., Zonnenberg B. A., Witteveen P. O. Totally implantable venous access devices: evaluation of complications and a prospective comparative study of two different port systems. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine . 2000;57(6):215–223. doi: 10.1016/s0300-2977(00)00083-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu D., Zhang C., Ji L., Ran R., Wu H., Xu Y. Forest fire recognition based on feature extraction from multi-view images. Traitement du Signal . 2021;38(3):775–783. doi: 10.18280/ts.380324. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

