Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in a Malaysian Preschooler
- PMID: 34877197
- PMCID: PMC8642153
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19207
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in a Malaysian Preschooler
Abstract
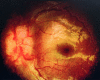
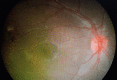
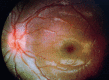
A four-year-old girl presented with a three-day history of squint and irritability. Examination showed reduced visual acuity in both eyes, the presence of a false localizing sign, and bilateral optic disc swelling. On investigation, her blood laboratory workup was within the normal range. Imaging of the brain showed no evidence of a space-occupying lesion or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. The lumbar puncture opening pressure was 27cmH20 and the cerebrospinal fluid workup was normal. The diagnosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) was made based on the diagnostic criteria for pseudotumor cerebri syndrome. She was successfully treated with acetazolamide with resolved symptoms and signs. This highlights the possibility of IIH presenting with inconspicuous symptoms in preschool children, which needs a high index suspicion by clinicians. Hence, solving the challenges in the workup, especially in children, is very crucial.
Keywords: false localizing sign; idiopathic intracranial hypertension (iih); papilledema; pediatric; pseudo tumor cerebri.
Copyright © 2021, Basiron et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Neurology. 2013;81:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Meta-analysis and systematic review of population-based epidemiological studies in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. McCluskey G, Doherty-Allan R, McCarron P, et al. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25:1218–1227. - PubMed
-
- Incidence and demographics of pediatric intracranial hypertension. Gillson N, Jones C, Reem RE, Rogers DL, Zumberge N, Aylward SC. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;73:42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
