Composition analysis and antioxidant activity evaluation of a high purity oligomeric procyanidin prepared from sea buckthorn by a green method
- PMID: 34877544
- PMCID: PMC8633577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.11.008
Composition analysis and antioxidant activity evaluation of a high purity oligomeric procyanidin prepared from sea buckthorn by a green method
Abstract
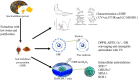
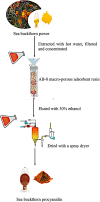
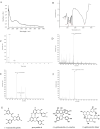
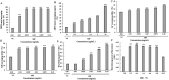
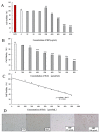
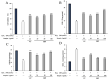
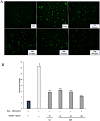
Procyanidin is an important polyphenol for its health-promoting properties, however, the study of procyanidin in sea buckthorn was limited. In this paper, sea buckthorn procyanidin (SBP) was obtained through a green isolation and enrichment technique with an extraction rate and purity of 9.1% and 91.5%. The structure of SBP was analyzed using Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The results show that SBP is an oligomeric procyanidin, mainly composed of (-)-epicatechin gallate, procyanidin B, (+)-gallocatechin-(+)-catechin, and (+)-gallocatechin dimer. SBP showed superior scavenging capacity on free radicals. Furthermore, the cleaning rate of the ABTS radical was 4.8 times higher than vitamin C at the same concentration. Moreover, SBP combined with vitamin C presented potent synergistic antioxidants with combined index values below 0.3 with concentration rates from 5:5 to 2:8. SBP also provided significant protection against oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on RAW264.7 cells. These findings prove the potential of SBP as a natural antioxidant in food additives and support the in-depth development of sea buckthorn resources.
Keywords: Antioxidative stress activity; Green preparation method; Oligomeric procyanidin; Sea buckthorn; Synergistic antioxidant.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alyethodi R.R., Sirohi A.S., Karthik S., Tyagi S., Perumal P., Singh U., Sharma A., Kundu A. Role of seminal MDA, ROS, and antioxidants in cryopreservation and their kinetics under the influence of ejaculatory abstinence in bovine semen. Cryobiology. 2021;98:187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2020.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashwin K., Pattanaik A.K., Howarth G.S. Polyphenolic bioactives as an emerging group of nutraceuticals for promotion of gut health: a review. Food Biosci. 2021;44 doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101376. - DOI
-
- Azmi L., Shukla I., Goutam A., Rao C.V., Jawaid T., Awaad A.S., Alqasoumi S.I., AlKhamees O.A., Kamal M. Oxidative free radicals scavenging activity (in vitro and in vivo assay) of standardized fractions from the seeds of Argyreia speciosa (Ghav-patta) a traditional Indian medicine. Saudi Pharmaceut. J. 2019;27(8):1210–1215. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.10.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai R., Cui Y., Luo L., Yuan D., Wei Z., Yu W., Sun B. A semisynthetic approach for the simultaneous reaction of grape seed polymeric procyanidins with catechin and epicatechin to obtain oligomeric procyanidins in large scale. Food Chem. 2019;278:609–616. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.091. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

