AXL targeting by a specific small molecule or monoclonal antibody inhibits renal cell carcinoma progression in an orthotopic mice model
- PMID: 34877810
- PMCID: PMC8652404
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15140
AXL targeting by a specific small molecule or monoclonal antibody inhibits renal cell carcinoma progression in an orthotopic mice model
Abstract
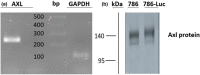
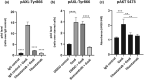
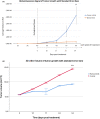
AXL tyrosine kinase activation enhances cancer cell survival, migration, invasiveness, and promotes drug resistance. AXL overexpression is typically detected in a high percentage of renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) and is strongly associated with poor prognosis. Therefore, AXL inhibition represents an attractive treatment option in these cancers. In this preclinical study, we investigated the antitumor role of a highly selective small molecule AXL inhibitor bemcentinib (BGB324, BerGenBio), and a newly developed humanized anti-AXL monoclonal function blocking antibody tilvestamab, (BGB149, BerGenBio), in vitro and an orthotopic RCC mice model. The 786-0-Luc human RCC cells showed high AXL expression. Both bemcentinib and tilvestamab significantly inhibited AXL activation induced by Gas6 stimulation in vitro. Furthermore, tilvestamab inhibited the downstream AKT phosphorylation in these cells. The 786-0-Luc human RCC cells generated tumors with high Ki67 and vimentin expression upon orthotopic implantation in athymic BALB/c nude mice. Most importantly, both bemcentinib and tilvestamab inhibited the progression of tumors induced by the orthotopically implanted 786-0 RCC cells. Remarkably, their in vivo antitumor effectiveness was not significantly enhanced by concomitant administration of a multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Bemcentinib and tilvestamab qualify as compounds of potentially high clinical interest in AXL overexpressing RCC.
Keywords: bemcentinib; orthotopic RCC; tilvestamab.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: M.B and G.G are employees from BerGenBio, Bergen, and have supplied the two AXL inhibiting agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Functional Role of GAS6/TAM in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression Implicates AXL as Therapeutic Target.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9(3):349-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.10.010. Epub 2019 Nov 2. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31689560 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOTAIR regulates HIF-1α/AXL signaling through inhibition of miR-217 in renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2017 May 11;8(5):e2772. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.181. Cell Death Dis. 2017. Retraction in: Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(10):716. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07111-9. PMID: 28492542 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Small molecule inhibition of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase potently suppresses multiple malignant properties of glioma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):16183-97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3952. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25980499 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma patients with cabozantinib, an oral multityrosine kinase inhibitor of MET, AXL and VEGF receptors.Future Oncol. 2019 Jul;15(20):2337-2348. doi: 10.2217/fon-2019-0021. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Future Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31184937 Review.
-
AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications.Mol Cancer. 2019 Nov 4;18(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1090-3. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31684958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two-Front War on Cancer-Targeting TAM Receptors in Solid Tumour Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 18;14(10):2488. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102488. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted degradation of MERTK and other TAM receptor paralogs by heterobifunctional targeted protein degraders.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1135373. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135373. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37545504 Free PMC article.
-
AXL signaling in cancer: from molecular insights to targeted therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Feb 10;10(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02121-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39924521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AXL Inhibitors: Status of Clinical Development.Curr Oncol Rep. 2023 May;25(5):521-529. doi: 10.1007/s11912-023-01392-7. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36920638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1 interactome in osteosarcoma: identification of a novel PD-1/AXL interaction conserved between humans and dogs.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 18;22(1):605. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01935-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39696578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blø, M. , Nilsson, L. H. , Jackson, A. , Boniecka, A. , Toombs, J. E. , Ahmed, L. , Mydel, P. M. , Marti, H. P. , Brekken, R. A. , Gabra, H. , Lorens, J. B. , Micklem, D. R. , & Gausdal, G. (2020). 160 Poster—Tilvestamab, a novel clinical stage humanized anti‐AXL function blocking antibody. European Journal of Cancer, 138, S44. 10.1016/S0959-8049(20)31192-8 - DOI
-
- Byers, L. A. , Diao, L. , Wang, J. , Saintigny, P. , Girard, L. , Peyton, M. , Shen, L. I. , Fan, Y. , Giri, U. , Tumula, P. K. , Nilsson, M. B. , Gudikote, J. , Tran, H. , Cardnell, R. J. G. , Bearss, D. J. , Warner, S. L. , Foulks, J. M. , Kanner, S. B. , Gandhi, V. , … Heymach, J. V. (2013). An epithelial‐mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3K Inhibitors and Identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clinical Cancer Research, 19(1), 279–290. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1558 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

