Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to treatment (Review)
- PMID: 34878154
- PMCID: PMC8711586
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5070
Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to treatment (Review)
Abstract
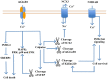
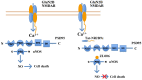
Stroke is the leading cause of disabilities and cognitive deficits, accounting for 5.2% of all mortalities worldwide. Transient or permanent occlusion of cerebral vessels leads to ischemic strokes, which constitutes the majority of strokes. Ischemic strokes induce brain infarcts, along with cerebral tissue death and focal neuronal damage. The infarct size and neurological severity after ischemic stroke episodes depends on the time period since occurrence, the severity of ischemia, systemic blood pressure, vein systems and location of infarcts, amongst others. Ischemic stroke is a complex disease, and neuronal injuries after ischemic strokes have been the focus of current studies. The present review will provide a basic pathological background of ischemic stroke and cerebral infarcts. Moreover, the major mechanisms underlying ischemic stroke and neuronal injuries are summarized. This review will also briefly summarize some representative clinical trials and up‑to‑date treatments that have been applied to stroke and brain infarcts.
Keywords: cerebral infarcts; clinical management; ischemic stroke; mechanism; neuronal injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

