Effect of empagliflozin in patients with heart failure across the spectrum of left ventricular ejection fraction
- PMID: 34878502
- PMCID: PMC8825259
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab798
Effect of empagliflozin in patients with heart failure across the spectrum of left ventricular ejection fraction
Abstract
Aims: No therapy has shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure across the entire range of ejection fractions seen in clinical practice. We assessed the influence of ejection fraction on the effect of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes.
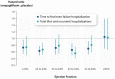
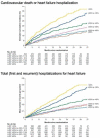
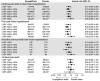
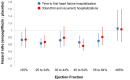
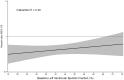
Methods and results: A pooled analysis was performed on both the EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved trials (9718 patients; 4860 empagliflozin and 4858 placebo), and patients were grouped based on ejection fraction: <25% (n = 999), 25-34% (n = 2230), 35-44% (n = 1272), 45-54% (n = 2260), 55-64% (n = 2092), and ≥65% (n = 865). Outcomes assessed included (i) time to first hospitalization for heart failure or cardiovascular mortality, (ii) time to first heart failure hospitalization, (iii) total (first and recurrent) hospitalizations for heart failure, and (iv) health status assessed by the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ). The risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure declined progressively as ejection fraction increased from <25% to ≥65%. Empagliflozin reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization, mainly by reducing heart failure hospitalizations. Empagliflozin reduced the risk of heart failure hospitalization by ≈30% in all ejection fraction subgroups, with an attenuated effect in patients with an ejection fraction ≥65%. Hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals were: ejection fraction <25%: 0.73 (0.55-0.96); ejection fraction 25-34%: 0.63 (0.50-0.78); ejection fraction 35-44%: 0.72 (0.52-0.98); ejection fraction 45-54%: 0.66 (0.50-0.86); ejection fraction 55-64%: 0.70 (0.53-0.92); and ejection fraction ≥65%: 1.05 (0.70-1.58). Other heart failure outcomes and measures, including KCCQ, showed a similar response pattern. Sex did not influence the responses to empagliflozin.
Conclusion: The magnitude of the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes was clinically meaningful and similar in patients with ejection fractions <25% to <65%, but was attenuated in patients with an ejection fraction ≥65%.
Key question: How does ejection fraction influence the effects of empagliflozin in patients with heart failure and either a reduced or a preserved ejection fraction?
Key finding: The magnitude of the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes and health status was similar in patients with ejection fractions <25% to <65%, but it was attenuated in patients with an ejection fraction ≥65%.
Take home message: The consistency of the response in patients with ejection fractions of <25% to <65% distinguishes the effects of empagliflozin from other drugs that have been evaluated across the full spectrum of ejection fractions in patients with heart failure.
Keywords: Ejection fraction; Empagliflozin; Hospitalization; Sex; Heart failure.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Re-emergence of heart failure with a normal ejection fraction?Eur Heart J. 2022 Feb 3;43(5):427-429. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab828. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 34878520 No abstract available.
References
-
- Butler J, Anker SD, Packer M. Redefining heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction. JAMA 2019;322:1761–1762. - PubMed
-
- Maggioni AP, Anand I, Gottlieb SO, Latini R, Tognoni G, Cohn JN; Val-HeFT Investigators (Valsartan Heart Failure Trial). Effects of valsartan on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure not receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40:1414–1421. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K et al.; CHARM Investigators and Committees. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved left-ventricular ejection fraction: the CHARM-Preserved Trial. Lancet 2003;362:777–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

