A MEKK1 - JNK mitogen activated kinase (MAPK) cascade module is active in Echinococcus multilocularis stem cells
- PMID: 34879059
- PMCID: PMC8687709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010027
A MEKK1 - JNK mitogen activated kinase (MAPK) cascade module is active in Echinococcus multilocularis stem cells
Abstract
Background: The metacestode larval stage of the fox-tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis by tumour-like growth within the liver of the intermediate host. Metacestode growth and development is stimulated by host-derived cytokines such as insulin, fibroblast growth factor, and epidermal growth factor via activation of cognate receptor tyrosine kinases expressed by the parasite. Little is known, however, concerning signal transmission to the parasite nucleus and cross-reaction with other parasite signalling systems.
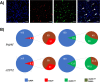
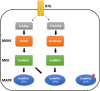
Methodology/principal findings: Using bioinformatic approaches, cloning, and yeast two-hybrid analyses we identified a novel mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) cascade module that consists of E. multilocularis orthologs of the tyrosine kinase receptor interactor Growth factor receptor-bound 2, EmGrb2, the MAPK kinase kinase EmMEKK1, a novel MAPK kinase, EmMKK3, and a close homolog to c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), EmMPK3. Whole mount in situ hybridization analyses indicated that EmMEKK1 and EmMPK3 are both expressed in E. multilocularis germinative (stem) cells but also in differentiated or differentiating cells. Treatment with the known JNK inhibitor SP600125 led to a significantly reduced formation of metacestode vesicles from stem cells and to a specific reduction of proliferating stem cells in mature metacestode vesicles.
Conclusions/significance: We provide evidence for the expression of a MEKK1-JNK MAPK cascade module which, in mammals, is crucially involved in stress responses, cytoskeletal rearrangements, and apoptosis, in E. multilocularis stem cells. Inhibitor studies indicate an important role of JNK signalling in E. multilocularis stem cell survival and/or maintenance. Our data are relevant for molecular and cellular studies into crosstalk signalling mechanisms that govern Echinococcus stem cell function and introduce the JNK signalling cascade as a possible target of chemotherapeutics against echinococcosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

