Very high prevalence of infection with the human T cell leukaemia virus type 1c in remote Australian Aboriginal communities: Results of a large cross-sectional community survey
- PMID: 34879069
- PMCID: PMC8654171
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009915
Very high prevalence of infection with the human T cell leukaemia virus type 1c in remote Australian Aboriginal communities: Results of a large cross-sectional community survey
Abstract
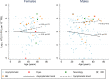
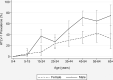
Infection with the human T cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) subtype C is endemic among Aboriginal people in central Australia. To provide insights into the risk factors for transmission, we conducted the first large-scale, community-based prevalence study in seven remote Aboriginal communities. Residents >2 years old were invited to participate in the study between August 2014 and June 2018. HTLV-1 infection was defined as a positive western blot (WB) test or a positive HTLV-1 PCR. 720 community residents participated in the study (children <15 years, 142; adults, 578). Prevalences for children and adults were 3.5% (5/142) and 36.8% (213/578), respectively, reaching 49.3% (106/215) for those older than 45 years. A wide range of proviral loads were measured for both asymptomatic and symptomatic participants with no difference within groups according to age or gender; however, median PVL was 1.34 log10 higher for symptomatic participants. The adult prevalence of HTLV-1 infection in central Australia is the highest reported worldwide. Sexual contact is likely to be the predominant mode of transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Plancoulaine S, Buigues RP, Murphy EL, van Beveren M, Pouliquen JF, Joubert M et al. Demographic and familial characteristics of HTLV-I infection among an isolated, highly endemic population of African origin in French Guiana. Int J Cancer. 1998. May 4;76(3):331–6. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19980504)76:3<331::aid-ijc8>3.0.co;2-w - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakashima K, Kahiwagi S., Kajiyama W., HIrata M., Hayashi J., Noguchi A et al. Sexual transmission of Human T-lymphotropic virus Type I among female prostitutes and among patients with sexually transmitted diseases in Fukuoka, Kyushu, Japan. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:305–311. doi: 10.1093/aje/141.4.305 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

