PNPLA3 downregulation exacerbates the fibrotic response in human hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 34879108
- PMCID: PMC8654208
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260721
PNPLA3 downregulation exacerbates the fibrotic response in human hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
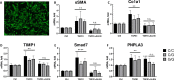
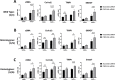
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) results, in part, from the interaction of metabolic derangements with predisposing genetic variants, leading to liver-related complications and mortality. The strongest genetic determinant is a highly prevalent missense variant in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3 p.I148M). In human liver hepatocytes PNPLA3 localizes to the surface of lipid droplets where the mutant form is believed to enhance lipid accumulation and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Less is known about the role of PNPLA3 in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Here we characterized HSC obtained from patients carrying the wild type (n = 8 C/C) and the heterozygous (n = 6, C/G) or homozygous (n = 6, G/G) PNPLA3 I148M and investigated the effect of genotype and PNPLA3 downregulation on baseline and TGF-β-stimulated fibrotic gene expression. HSCs from all genotypes showed comparable baseline levels of PNPLA3 and expression of the fibrotic genes α-SMA, COL1A1, TIMP1 and SMAD7. Treatment with TGF-β increased PNPLA3 expression in all 3 genotypes (~2-fold) and resulted in similar stimulation of the expression of several fibrogenic genes. In primary human HSCs carrying wild-type (WT) PNPLA3, siRNA treatment reduced PNPLA3 mRNA by 79% resulting in increased expression of α-SMA, Col1a1, TIMP1, and SMAD7 in cells stimulated with TGF-β. Similarly, knock-down of PNPLA3 in HSCs carrying either C/G or G/G genotypes resulted in potentiation of TGF-β induced expression of fibrotic genes. Knockdown of PNPLA3 did not impact fibrotic gene expression in the absence of TGF-β treatment. Together, these data indicate that the presence of the I148M PNPLA3 mutation in HSC has no effect on baseline activation and that downregulation of PNPLA3 exacerbates the fibrotic response irrespective of the genotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PNPLA3 I148M Up-Regulates Hedgehog and Yap Signaling in Human Hepatic Stellate Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 18;21(22):8711. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228711. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33218077 Free PMC article.
-
PNPLA3 has retinyl-palmitate lipase activity in human hepatic stellate cells.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Aug 1;23(15):4077-85. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu121. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24670599 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of the PNPLA3 I148M variant on primary human hepatic stellate cells using 3D extracellular matrix models.J Hepatol. 2024 Jun;80(6):941-956. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.01.032. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38365182
-
Role of PNPLA3 in Hepatic Stellate Cells and Hepatic Cellular Crosstalk.Liver Int. 2025 Apr;45(4):e16117. doi: 10.1111/liv.16117. Epub 2024 Oct 12. Liver Int. 2025. PMID: 39394864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed Vitamin A Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).Nutrients. 2017 Dec 29;10(1):29. doi: 10.3390/nu10010029. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29286303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The State of the Art Update.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Nov;22(11):2177-2187.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.05.052. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39094912 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cell activation markers are regulated by the vagus nerve in systemic inflammation.Bioelectron Med. 2023 Mar 31;9(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s42234-023-00108-3. Bioelectron Med. 2023. PMID: 36997988 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrosis: cross-organ biology and pathways to development of innovative drugs.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Jul;24(7):543-569. doi: 10.1038/s41573-025-01158-9. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40102636 Review.
-
Gut microbes, diet, and genetics as drivers of metabolic liver disease: a narrative review outlining implications for precision medicine.J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Nov;133:109704. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109704. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Nutr Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39029595 Review.
-
Exploring the role of genetic variations in NAFLD: implications for disease pathogenesis and precision medicine approaches.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 20;29(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01708-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38504356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valenti L, Al-Serri A, Daly AK, Galmozzi E, Rametta R, Dongiovanni P, et al.. 2010. Homozygosity for the patatin-like phospholipase-3/adiponutrin I148M polymorphism influences liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. Apr;51(4):1209–17. doi: 10.1002/hep.23622 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

