Cardiometabolic health benefits of dairy-milk polar lipids
- PMID: 34879146
- PMCID: PMC8653938
- DOI: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab085
Cardiometabolic health benefits of dairy-milk polar lipids
Abstract
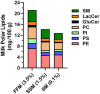
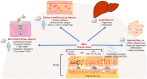
Low-quality dietary patterns impair cardiometabolic health by increasing the risk of obesity-related disorders. Cardiometabolic risk relative to dairy-food consumption continues to be a controversial topic, due to recommendations that endorse low-fat and nonfat dairy foods over full-fat varieties despite accumulated evidence that does not strongly support these recommendations. Controlled human studies and mechanistic preclinical investigations support that full-fat dairy foods decrease cardiometabolic risk by promoting gut health, reducing inflammation, and managing dyslipidemia. These gut- and systemic-level cardiometabolic benefits are attributed, at least in part, to milk polar lipids (MPLs) derived from the phospholipid- and sphingolipid-rich milk fat globule membrane that is of higher abundance in full-fat dairy milk. The controversy surrounding full-fat dairy food consumption is discussed in this review relative to cardiometabolic health and MPL bioactivities that alleviate dyslipidemia, shift gut microbiota composition, and reduce inflammation. This summary, therefore, is expected to advance the understanding of full-fat dairy foods through their MPLs and the need for translational research to establish evidence-based dietary recommendations.
Keywords: dairy milk; milk fat globule membrane; milk phospholipids; milk polar lipids; milk sphingomyelin.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Life Sciences Institute.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Standl E, Khunti K, Hansen TB, et al. The global epidemics of diabetes in the 21st century: current situation and perspectives. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;26:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. ; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. - PubMed
-
- Drewnowski A. The Nutrient Rich Foods Index helps to identify healthy, affordable foods. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:1095S–1101S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

