Outcomes of atrial fibrillation in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34879483
- PMCID: PMC8483996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.09.050
Outcomes of atrial fibrillation in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Recently, emerging evidence has suggested that atrial fibrillation (AF) has an epidemiological correlation with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the clinical outcomes of AF in COVID-19 remain inconsistent and inconclusive. The aim of this study was to provide a comprehensive description of the impact of AF on the prognosis of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
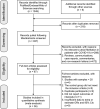
Methods: Three electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science) were searched for eligible studies as of March 1, 2021. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to evaluate the associations between AF (preexisting and new-onset) and in-hospital mortality, post-discharge mortality, and ventilator use.
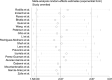
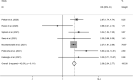
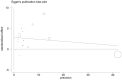
Results: A total of 36 individual studies were incorporated into our meta-analysis. The combined results revealed that preexisting AF was associated with increased in-hospital mortality (pooled OR: 2.07; 95% CI: 1.60-2.67; p < 0.001), post-discharge mortality (pooled OR: 2.69; 95% CI: 1.24-5.83; p < 0.05), and ventilator utilization (pooled OR: 4.53; 95% CI: 1.33-15.38; p < 0.05) in patients with COVID-19. In addition, our data demonstrated that new-onset AF during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection was significantly correlated with increased mortality (pooled OR: 2.38; 95% CI: 2.04-2.77; p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The presence of AF is correlated with adverse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, which deserves increased attention and should be managed appropriately to prevent adverse outcomes.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Atrial fibrillation; COVID-19; Meta-analysis; Mortality.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Atrial fibrillation in COVID-19 patients receiving remdesivir, matched case-control analysis.Am J Emerg Med. 2022 Sep;59:182-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.051. Epub 2022 May 10. Am J Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35577624 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The impact of atrial fibrillation on outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.Eur J Intern Med. 2023 May;111:127-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2023.01.017. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Eur J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36710138 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

