Epidemiological trends of urinary tract infections, urolithiasis and benign prostatic hyperplasia in 203 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
- PMID: 34879880
- PMCID: PMC8656041
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-021-00359-8
Epidemiological trends of urinary tract infections, urolithiasis and benign prostatic hyperplasia in 203 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infections (UTI), urolithiasis, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) are three of the most common nonmalignant conditions in urology. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive and updated epidemiological data. This study aimed to investigate the disease burden of UTI, urolithiasis, and BPH in 203 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019.
Methods: Data were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease 2019, including incident cases, deaths, disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) and corresponding age-standardized rate (ASR) from 1990 to 2019. Estimated annual percentage changes (EAPC) were calculated to evaluate the trends of ASR. The associations between disease burden and social development degrees were analyzed using a sociodemographic index (SDI).
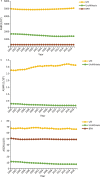
Results: Compared with 1990, the incident cases of UTI, urolithiasis, and BPH increased by 60.40%, 48.57%, and 105.70% in 2019, respectively. The age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of UTI increased (EAPC = 0.08), while urolithiasis (EAPC = - 0.83) and BPH (EAPC = - 0.03) decreased from 1990 to 2019. In 2019, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) of UTI and urolithiasis were 3.13/100,000 and 0.17/100,000, respectively. BPH had the largest increase (110.56%) in DALYs in the past three decades, followed by UTI (68.89%) and urolithiasis (16.95%). The burden of UTI was mainly concentrated in South Asia and Tropical Latin America, while the burden of urolithiasis and BPH was recorded in Asia and Eastern Europe. Moreover, the ASIR and SDI of urolithiasis in high-SDI regions from 1990 to 2019 were negatively correlated, while the opposite trend was seen in low-SDI regions. In 2019, the ASIR of UTI in females was 3.59 times that of males, while the ASIR of urolithiasis in males was 1.96 times higher than that in females. The incidence was highest in the 30-34, 55-59, and 65-69 age groups among the UTI, urolithiasis, and BPH groups, respectively.
Conclusion: Over the past three decades, the disease burden has increased for UTI but decreased for urolithiasis and BPH. The allocation of medical resources should be based more on the epidemiological characteristics and geographical distribution of diseases.
Keywords: Benign prostatic hyperplasia; Disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs); Disease burden; Incidence; Mortality; Urinary tract infections; Urolithiasis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

