Efficacy of Ligustrazine Injection as Adjunctive Therapy in Treating Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34880757
- PMCID: PMC8646035
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761722
Efficacy of Ligustrazine Injection as Adjunctive Therapy in Treating Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
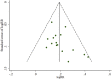
Background: Ligustrazine injection has been widely used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction (ACI) during the past decades in China, but its clinical efficacy is not yet well confirmed. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of ligustrazine injection as adjunctive therapy for ACI. Methods: Databases including China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Science and Technology Journal Database (VIP), PubMed, Medline, Google Scholar, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, Cochrane Library, Embase, Sino-Med, Wanfang Database, and Chinese Science Citation Database were systematically searched for the published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on ligustrazine injection in the treatment of ACI until November 2020. Meta-analysis was performed on the primary outcome measure (i.e., clinical effective rate) and the secondary outcome measure [i.e., neurological deficit score (NDS), fibrinogen, low shear blood viscosity (LBV), and high shear blood viscosity (HBV)]. The quality of the included RCTs was assessed according to the M scoring system (the refined Jadad scale). Sensitivity analysis and subgroup analysis were conducted according to the methodological quality, years of publication, and sample size. Results: Nineteen RCTs, containing 2022 patients, were included in this study. Meta-analysis indicated that ligustrazine injection combined with Western medicine could achieve a better effect in the treatment of ACI than using Western medicine alone in terms of clinical effective rate (RR = 1.24; 95% CI, 1.19-1.29), NDS (MD = -3.88; 95%CI, -4.51 to -3.61), fibrinogen (MD = -0.59; 95% CI, -0.76 to -0.42), LBV (MD = -2.11; 95% CI, -3.16 to -1.06), and HBV (MD = -0.88; 95% CI, -1.20 to -0.55). Conclusions: This research indicated that ligustrazine injection as adjunctive therapy seemed to be more effective than using western medicine alone in treating ACI. However, more evidence is required to confirm the efficacy of ligustrazine injection due to the low methodological quality of the included RCTs.
Keywords: acute cerebral infarction; adjunctive therapy; ligustrazine injection; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2021 Shao, He, Zhang, Du, Yi, Cui, Liu, Huang and Tong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- CAST (Chinese Acute Stroke Trial) Collaborative Group (1997). CAST: Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial of Early Aspirin Use in 20,000 Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke. CAST (Chinese Acute Stroke Trial) Collaborative Group. Lancet 349, 1641–1649. - PubMed
-
- Chang S. W. (2011). Clinical Observation of Ozagrel Sodium Injection Combined with Ligustrazine Injection in the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction. Chin. J. Pract. Nerv. Dis. 14, 46–47. (In Chinese). 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2011.17.022 - DOI
-
- Chen Z. J., Wen X. (2012). Study on the Effect of Fibrinogenase Injection Combined with Ligustrazine Injection in Treating Acute Cerebral Infarction Patients. Guide China Med. 10, 294–295. (In Chinese). 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2012.19.211 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

