Breakfast Consumption and Academic Achievement Among Chinese Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model
- PMID: 34880802
- PMCID: PMC8647908
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.700989
Breakfast Consumption and Academic Achievement Among Chinese Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model
Abstract
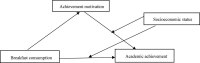
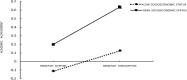
The studies have shown that a healthy lifestyle has a significant impact on the academic achievement of adolescents. Behavior of breakfast eating is considered a hallmark of dietary patterns and an important component of a healthy lifestyle. The prior study explained that students had a lower level of achievement motivation at school because they were exposed to some militating factors in their families such as absenteeism, ill health, malnutrition, and hunger. This study examined the mediating role of achievement motivation and moderating role of socioeconomic status (SES) in the association between breakfast consumption and academic achievement. This study used a sample of 15-year-old Chinese students who participated in Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) 2015. In terms of gender, female students accounted for 47.2% and male students accounted for 52.8%. The results showed that (1) breakfast consumption had a positive predictive effect on academic achievement; (2) achievement motivation played a partial mediating role in the relationship between breakfast consumption and academic achievement; and (3) the direct and indirect effects were moderated by the SES of students, which meant that the effect of breakfast consumption on achievement motivation can differ depending on the SES of students. Besides, both the effects were stronger for individuals with higher SES. The conclusion of this study has an important theoretical value and reference value to guide the Chinese parents and Chinese adolescents to pay more attention to breakfast consumption and healthy lifestyles.
Keywords: Chinese adolescents; academic achievement; achievement motivation; breakfast consumption; mediating effect; moderating effect; socioeconomic status.
Copyright © 2021 Gao, Zhao and Shu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Acharya N., Joshi S. (2009). Influence of parents’ education on achievement motivation of adolescents. Indian J. Soc. Sci. Res. 6 72–79.
-
- Affenito S. G. (2007). Breakfast: a missed opportunity. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 107 565–569. - PubMed
-
- Affenito S. G., Thompson D. R., Barton B. A., Franko D. L., Daniels S. R., Obarzanek E., et al. (2005). Breakfast consumption by African-American and white adolescent girls correlates positively with calcium and fiber intake and negatively with body mass index. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 105 938–945. 10.1016/j.jada.2005.03.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources