Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Stroke in China From 1990 to 2019
- PMID: 34880825
- PMCID: PMC8645546
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.759221
Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Stroke in China From 1990 to 2019
Abstract
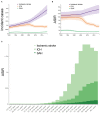
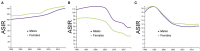
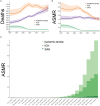
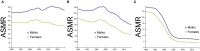
Objective: Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity globally. This study aimed to analyze the burden and 30-year trends of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) in China. Methods: Data that include incidence and mortality of stroke in China from January 1, 1990 to December 31, 2019 were derived from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 2019. The absolute numbers of incident cases and deaths over the time, and age-standardized rates per 100,000, such as age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) and age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), were analyzed. Results: In 2019, there were 3.9 (95% uncertainty intervals (UI) 3.4-4.5) million incident cases and 2.1 (3.4-4.5) million deaths related to stroke in China. The ASIR and ASMR of stroke in China was 200 (176-230) and 127 (110-144). From 1990 to 2019, the ASIR of ischemic stroke had increased by 35.0% (29.0-40.0) while the ASIR of ICH and SAH had decreased by -53.0% (-56.0 to -50.0) and by -39.0% (-44.0 to -35.0), respectively. The ASMR of ischemic stroke had increased by 3.0% (-26.0 to 16.0) while the ASMR of ICH and SAH had decreased by -48.0% (-59.0 to -38.0) and by -84.0% (-89.0 to -69.0), respectively. Conclusion: Although the incidence and mortality rates of stroke in China were decreased from 1990 to 2019, the number of incident cases and deaths nearly doubled. A sharp increase in the incidence rate of ischemic stroke was observed. A higher incidence rate of ischemic stroke in the women was also observed.
Keywords: burden; incidence; mortality; stroke; trends.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Chen, Wu, Sun, Zhang and You.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in hemorrhagic stroke incidence and mortality in a National Stroke Registry of a multi-ethnic Asian population.Eur Stroke J. 2024 Mar;9(1):189-199. doi: 10.1177/23969873231202392. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Eur Stroke J. 2024. PMID: 37776052 Free PMC article.
-
Global, Regional and Country-Specific Burden of Ischaemic Stroke, Intracerebral Haemorrhage and Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.Neuroepidemiology. 2020;54(2):171-179. doi: 10.1159/000506396. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Neuroepidemiology. 2020. PMID: 32079017
-
Analysis of the burden of intracerebral hemorrhage in the Asian population aged 45 and older and ARIMA model prediction trends: a systematic study based on the GBD 2021.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 13;16:1526524. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1526524. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40027166 Free PMC article.
-
The global burden of ischemic stroke: findings of the GBD 2010 study.Glob Heart. 2014 Mar;9(1):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gheart.2014.01.001. Glob Heart. 2014. PMID: 25432120 Review.
-
The global burden of hemorrhagic stroke: a summary of findings from the GBD 2010 study.Glob Heart. 2014 Mar;9(1):101-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gheart.2014.01.003. Glob Heart. 2014. PMID: 25432119 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Optimization of an Adaptive Knee Joint Orthosis for Biomimetic Motion Rehabilitation Assistance.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;9(2):98. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9020098. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392144 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of life expectancy due to stroke and its subtypes in urban and rural areas in China, 2005-2020.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2023 Oct;8(5):349-357. doi: 10.1136/svn-2022-001968. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36878612 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors influencing cognitive impairment among the older adult stroke survivors: a cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 15;11:1254126. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1254126. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37790718 Free PMC article.
-
Relative and absolute inequalities in cerebrovascular disease mortality rates: exploring the influence of socioeconomic status and urbanization levels in Taiwan.BMC Public Health. 2024 Apr 27;24(1):1186. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18679-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38678225 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in hemorrhagic stroke incidence and mortality in a National Stroke Registry of a multi-ethnic Asian population.Eur Stroke J. 2024 Mar;9(1):189-199. doi: 10.1177/23969873231202392. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Eur Stroke J. 2024. PMID: 37776052 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

