CD247, a Potential T Cell-Derived Disease Severity and Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 34880861
- PMCID: PMC8645971
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.762594
CD247, a Potential T Cell-Derived Disease Severity and Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has high mortality worldwide. The CD247 molecule (CD247, as known as T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 zeta chain) has been reported as a susceptibility locus in systemic sclerosis, but its correlation with IPF remains unclear.
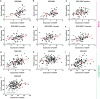
Methods: Datasets were acquired by researching the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). CD247 was identified as the hub gene associated with percent predicted diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (Dlco% predicted) and prognosis according to Pearson correlation, logistic regression, and survival analysis.
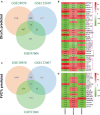
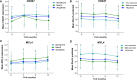
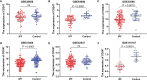
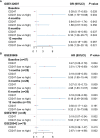
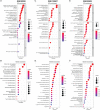
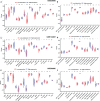
Results: CD247 is significantly downregulated in patients with IPF compared with controls in both blood and lung tissue samples. Moreover, CD247 is significantly positively associated with Dlco% predicted in blood and lung tissue samples. Patients with low-expression CD247 had shorter transplant-free survival (TFS) time and more composite end-point events (CEP, death, or decline in FVC >10% over a 6-month period) compared with patients with high-expression CD247 (blood). Moreover, in the follow-up 1st, 3rd, 6th, and 12th months, low expression of CD247 was still the risk factor of CEP in the GSE93606 dataset (blood). Thirteen genes were found to interact with CD247 according to the protein-protein interaction network, and the 14 genes including CD247 were associated with the functions of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells such as PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway and NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Furthermore, we also found that a low expression of CD247 might be associated with a lower activity of TIL (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes), checkpoint, and cytolytic activity and a higher activity of macrophages and neutrophils.
Conclusion: These results imply that CD247 may be a potential T cell-derived disease severity and prognostic biomarker for IPF.
Keywords: CD247; biomarker; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; immune response; inflammation response; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Chen, Li, Wang, Li, Ning and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
S100A12 as Biomarker of Disease Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 4;13:810338. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810338. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185901 Free PMC article.
-
CD247, a novel T cell-derived diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for detecting disease progression and severity in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2015 Jan;38(1):113-8. doi: 10.2337/dc14-1544. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Diabetes Care. 2015. PMID: 25368105
-
Peripheral blood proteomic profiling of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis biomarkers in the multicentre IPF-PRO Registry.Respir Res. 2019 Oct 22;20(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1190-z. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31640794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proportions of resting memory T cells and monocytes in blood have prognostic significance in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Genomics. 2019 Dec;111(6):1343-1350. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30261315 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in CD247.Scand J Immunol. 2022 Jul;96(1):e13170. doi: 10.1111/sji.13170. Epub 2022 Apr 17. Scand J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35388926 Review.
Cited by
-
Candidate Genetic Loci Modifying the Colorectal Cancer Risk Caused by Lifestyle Risk Factors.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 1;16(1):e00790. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000790. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39665592 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling reveals candidate biomarkers and probable molecular mechanisms in chronic stress.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6048-6060. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2040872. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35184642 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the mechanisms of serplulimab: a distinctive anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, in combination with a TIGIT or LAG3 inhibitor in preclinical tumor immunotherapy studies.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2419838. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2419838. Epub 2024 Nov 4. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39497266 Free PMC article.
-
Novel kinase 1 regulates CD8+T cells as a potential therapeutic mechanism for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 22;21(6):1079-1090. doi: 10.7150/ijms.93510. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38774751 Free PMC article.
-
5-methyladenosine regulators play a crucial role in development of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 12;13(1):5941. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32452-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37045913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King TE, Jr, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, du Bois RM, Leff JA, et al. . All-Cause Mortality Rate in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Implications for the Design and Execution of Clinical Trials. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2014) 189(7):825–31. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201311-1951OC - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

