Electroacupuncture Regulates TRPV1 through PAR2/PKC Pathway to Alleviate Visceral Hypersensitivity in FD Rats
- PMID: 34880917
- PMCID: PMC8648456
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1975228
Electroacupuncture Regulates TRPV1 through PAR2/PKC Pathway to Alleviate Visceral Hypersensitivity in FD Rats
Abstract
Visceral hypersensitivity (VH) is the predominant pathogenesis of functional dyspepsia (FD). Duodenal hypersensitivity along with nausea further reduces the comfort level in gastric balloon dilatation and inhibits gastric receptive relaxation. The potential mechanism behind electroacupuncture- (EA-) mediated alleviation of VH has not been elucidated. In an FD rat model with tail clamping stress, iodine acetamide (IA) induced VH. The rats were treated with EA with or without PAR2 antagonist FSLLRY-NH2, and the body weight, gastric sensitivity, compliance, and gastrointestinal motility were determined. Mast cells and activated degranulation were stained with toluidine blue (TB) staining and visualized under a transmission electron microscope (TEM). Immunofluorescence was used to detect the expression of PAR2, PKC, and TRPV1 in the duodenum and dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and that of CGRP, SP in DRG, and c-fos in the spinal cord. EA alone and EA + antagonist enhanced the gastrointestinal motility but diminished the expression of TRPV1, CGRP, SP, and c-fos-downstream of PAR2/PKC pathway and alleviated VH in FD rats. However, there was no obvious superposition effect between the antagonists and EA + antagonists. The effect of EA alone was better than that of antagonists and EA + antagonists 2 alone. EA-induced amelioration of VH in FD rats was mediated by TRPV1 regulation through PAR2/PKC pathway. This protective mechanism involved several pathways and included several targets.
Copyright © 2021 Yong-li Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
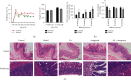


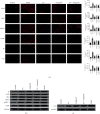
Similar articles
-
Butyrate promotes visceral hypersensitivity in IBS model via mast cell-derived DRG neuron lincRNA-01028-PKC-TRPV1 pathway.mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0153324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01533-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38953358 Free PMC article.
-
[Influence of electroacupuncture of"Zusanli"(ST36)on mast cells/TRPV1 signaling pathway in visceral hypersensitivity rats with functional dyspepsia].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Jul 25;47(7):592-7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210937. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35880275 Chinese.
-
Mechanisms of Probiotic VSL#3 in a Rat Model of Visceral Hypersensitivity Involves the Mast Cell-PAR2-TRPV1 Pathway.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 May;64(5):1182-1192. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5416-6. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30560330
-
Electroacupuncture for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 6;99(45):e23014. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023014. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33157947 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture and electroacupuncture for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 21;26(19):2440-2457. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2440. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32476804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Butyrate promotes visceral hypersensitivity in IBS model via mast cell-derived DRG neuron lincRNA-01028-PKC-TRPV1 pathway.mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0153324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01533-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38953358 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-effective characteristics and advantages of acupuncture in COVID-19 treatment.Acupunct Herb Med. 2023 Jun;3(2):83-95. doi: 10.1097/HM9.0000000000000062. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Acupunct Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 37810368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture Relieves Visceral Hypersensitivity via Balancing PAR2 and PAR4 in the Descending Pain Modulatory System of Goats.Brain Sci. 2023 Jun 7;13(6):922. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13060922. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37371401 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

