Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis of the Underlying Mechanism of Hyssopus cuspidatus Boriss. for Antiasthma: A Characteristic Medicinal Material in Xinjiang
- PMID: 34880921
- PMCID: PMC8648465
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7671247
Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis of the Underlying Mechanism of Hyssopus cuspidatus Boriss. for Antiasthma: A Characteristic Medicinal Material in Xinjiang
Abstract
Background: Hyssopus cuspidatus Boriss. (Shen Xiang Cao (SXC)), a traditional medicine herb in Xinjiang, has a long history of being used by minorities to treat asthma. However, its active antiasthmatic compounds and underlying mechanism of action are still unknown. The aim of this study was to investigate the bioactive compounds and explore the molecular mechanism of SCX in the treatment of asthma using network pharmacology.
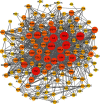
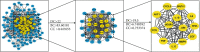
Methods: The compounds of SCX were collected by a literature search, and Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) and SwissTargetPrediction were used to predict targets and screen active compounds. Moreover, asthma-related targets were obtained based on DisGeNET, Herb, and GeneCards databases, and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was built by the STRING database. Furthermore, the topological analysis of the PPI and SXC-compound-target networks were analyzed and established by Cytoscape software. Finally, the RStudio software package was used for carrying out Gene Ontology (GO) function enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis. AutoDock tools and AutoDock Vina were used to molecularly dock the active compounds and key targets.
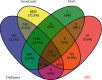
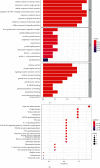
Results: A total of 8 active compounds and 258 potential targets related to SXC were predicted, and PPI network screened out key targets, including IL-6, JUN, TNF, IL10, and CXCL8. GO enrichment analysis involved cell responses to reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress, chemical stress, etc. In addition, KEGG pathway analysis showed that SXC effectively treated asthma through regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathways, interleukin 17 (IL-17) signaling pathways, toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathways, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathways.
Conclusion: The preliminary study that was based on multiple compounds, multiple targets, and multiple pathways provides a scientific basis for further elucidating the molecules involved and the underlying antiasthma-related mechanisms of SXC.
Copyright © 2021 Rongchang Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploration of the Molecular Mechanisms of Hyssopus cuspidatus Boriss Treatment of Asthma in an mRNA-miRNA Network via Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 5;2022:7111901. doi: 10.1155/2022/7111901. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35572723 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Mechanism of Guizhi to Treat Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 27;2021:8141075. doi: 10.1155/2021/8141075. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34873575 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza in diabetic nephropathy using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jun 25;41(6):BSR20203520. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203520. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33634308 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
The Genus Hyssopus: Traditional Use, Phytochemicals and Pharmacological Properties.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;13(12):1683. doi: 10.3390/plants13121683. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the Underlying Mechanism of Acacia Nilotica against Asthma from a Systematic Perspective: A Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Study.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;13(2):411. doi: 10.3390/life13020411. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836768 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

