Intestinal Inflammation and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 34881085
- PMCID: PMC8612622
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2021.0418
Intestinal Inflammation and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
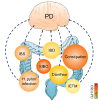
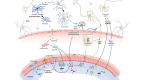
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease which significantly influences the life quality of patients. The protein α-synuclein plays an important driving role in PD occurrence and development. Braak's hypothesis suggests that α-synuclein is produced in intestine, and then spreads into the central nervous system through the vagus nerve. The abnormal expression of α-synuclein has been found in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Intestinal inflammation and intestinal dysbiosis have been involved in the occurrence and development of PD. The present review aimed to summarize recent advancements in studies focusing on intestinal inflammation and PD, especially the mechanisms through which link intestinal inflammation and PD. The intestinal dysfunctions such as constipation have been introduced as non-motor manifestations of PD. The possible linkages between IBD and PD, including genetic overlaps, inflammatory responses, intestinal permeability, and intestinal dysbiosis, are mainly discussed. Although it is not confirmed whether PD starts from intestine, intestinal dysfunction may affect intestinal microenvironment to influence central nervous system, including the α-synuclein pathologies and systematic inflammation. It is expected to develop some new strategies in the diagnosis and treatment of PD from the aspect of intestine. It may also become an exciting direction to find better ways to regulate the composition of gut microorganism to treat PD.
Keywords: Inflammation; Parkinson’s disease; inflammatory bowel disease; microbiota.
Copyright: © 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Opara J, Malecki A, Malecka E, Socha T (2017). Motor assessment in Parkinson`s disease. Ann Agric Environ Med, 24:411-415. - PubMed
-
- Khedr EM, El Fetoh NA, Khalifa H, Ahmed MA, El Beh KM (2013). Prevalence of non motor features in a cohort of Parkinson's disease patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 115:673-677. - PubMed
-
- Fu P, Gao M, Yung KKL (2020). Association of Intestinal Disorders with Parkinson's Disease and Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. ACS Chem Neurosci, 11:395-405. - PubMed
-
- Rezaie A, Gu P, Kaplan GG, Pimentel M, Al-Darmaki AK (2018). Dyssynergic Defecation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 24:1065-1073. - PubMed
-
- Bencsik A, Muselli L, Leboidre M, Lakhdar L, Baron T (2014). Early and persistent expression of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in the enteric nervous system of A53T mutant human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 73:1144-1151. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
