Correlation Between Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Myocardial Injury in Population Exposed to High Altitude
- PMID: 34881301
- PMCID: PMC8645565
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.738817
Correlation Between Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Myocardial Injury in Population Exposed to High Altitude
Abstract
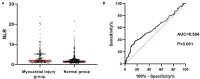
Objective: Myocardial injury is a severe complication in population exposed to high altitude. As a new biomarker for inflammatory response, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been widely used to predict the prognosis of various diseases. In this study, we intend to explore the risk factors for myocardial injury at high altitude and examine the relationship between NLR level and development of myocardial injury. Methods: Consecutive patients admitted to a secondary general hospital at high altitude from June 2019 to May 2020 were selected into this retrospective study. Clinical and biochemical data were collected. According to the results of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase isoenzymes (CK-MB), and aspartate amino transferase (AST), patients were divided into myocardial injury group and normal group. Results: A total of 476 patients were enrolled in this study. Myocardial injury occurred in 158 patients (33.2%). We found that altitude, NLR, hemoglobin, total bilirubin, total cholesterol, and lipoprotein A in myocardial injury group were significantly higher than that in normal group (P < 0.05), while platelet count in myocardial injury group was significantly lower than that in normal group (P < 0.05). Logistic multivariate regression analysis revealed that there was an independent relationship between myocardial injury and smoke, NLR, hemoglobin (P < 0.05). By using Spearman correlation analysis, NLR was proved to have a significant positive correlation with LDH, CK, and CK-MB (P < 0.05) instead of AST. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn to demonstrate that NLR could significantly predict the occurrence of myocardial injury with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.594 (95% CI: 0.537-0.650, P < 0.05), and the level of 2.967 (sensitivity = 38.0%, specificity = 83.6%) was optimal cutoff value. Conclusion: The incidence of myocardial injury is high in population at high altitude. Smoke, hemoglobin, and NLR are independent factors related to myocardial injury. As a convenient and efficient marker, NLR is found to be closely associated with myocardial enzymes and have a predict role in the occurrence of myocardial injury. This study will provide a theoretical basis on NLR for the early diagnosis of myocardial injury at high altitude.
Keywords: high altitude; myocardial enzymes; myocardial injury; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; predictor.
Copyright © 2021 He, He, Yang, Li, Gao, Xie and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Analysis of Myocardial Injury in Highlanders with Pulmonary Hypertension.High Alt Med Biol. 2024 Sep;25(3):205-211. doi: 10.1089/ham.2023.0075. Epub 2024 Jun 20. High Alt Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38900692
-
[Predictive value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with soluble growth stimulating expression gene 2 protein on the occurrence of in-hospital major adverse cardiaovascular events in patients with myocardial injury from moderate-severe acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a single-center prospective observational study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Sep;33(9):1088-1093. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210410-00273. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34839867 Chinese.
-
Risk assessment of severe adult tetanus using the NLR and AST level and construction of a nomogram prediction model.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 12;10(1):e23487. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23487. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38173491 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio on myocardial injury in severe COVID-19 patients].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 24;48(7):572-579. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20200422-00336. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842269 Chinese.
-
[Relationship between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and myocardial injury induced by acute carbon monoxide poisoning].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2018 May 20;36(5):362-364. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2018.05.010. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29996382 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Core Role of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio to Predict All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality: A Research of the 2005-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 12;9:847998. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.847998. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35647067 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of altitude and exercise intensity on cardiac function in rats.Exp Physiol. 2025 May;110(5):735-743. doi: 10.1113/EP092037. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39325671 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of muscle necrosis in patients with acute compartment syndrome.Int Orthop. 2023 Apr;47(4):905-913. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05699-9. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Int Orthop. 2023. PMID: 36715712 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate counteracting the chronic hypobaric hypoxia-induced myocardial injury in plain-grown rats at high altitude.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):921-933. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01386-1. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37875765 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and risk factors of severe acute high-altitude illness in healthy adults first entering the northern Tibetan Plateau of over 5,000 m.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 9;12:1400236. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1400236. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39319295 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

