Disease Burden Affects Outcomes in Pediatric and Young Adult B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia After Commercial Tisagenlecleucel: A Pediatric Real-World Chimeric Antigen Receptor Consortium Report
- PMID: 34882493
- PMCID: PMC9384925
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.03585
Disease Burden Affects Outcomes in Pediatric and Young Adult B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia After Commercial Tisagenlecleucel: A Pediatric Real-World Chimeric Antigen Receptor Consortium Report
Abstract
Purpose: Tisagenlecleucel is a CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, US Food and Drug Administration-approved for children, adolescents, and young adults (CAYA) with relapsed and/or refractory (RR) B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). The US Food and Drug Administration registration for tisagenlecleucel was based on a complete response (CR) rate of 81%, 12-month overall survival (OS) of 76%, and event-free survival (EFS) of 50%. We report clinical outcomes and analyze covariates of outcomes after commercial tisagenlecleucel.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, multi-institutional study of CAYA with RR B-ALL across 15 US institutions, who underwent leukapheresis shipment to Novartis for commercial tisagenlecleucel. A total of 200 patients were included in an intent-to-treat response analysis, and 185 infused patients were analyzed for survival and toxicity.
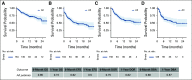
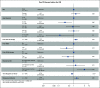
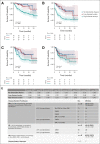
Results: Intent-to-treat analysis demonstrates a 79% morphologic CR rate (95% CI, 72 to 84). The infused cohort had an 85% CR (95% CI, 79 to 89) and 12-month OS of 72% and EFS of 50%, with 335 days of median follow-up. Notably, 48% of patients had low-disease burden (< 5% bone marrow lymphoblasts, no CNS3, or other extramedullary disease), or undetectable disease, pretisagenlecleucel. Univariate and multivariate analyses associate high-disease burden (HB, ≥ 5% bone marrow lymphoblasts, CNS3, or non-CNS extramedullary) with inferior outcomes, with a 12-month OS of 58% and EFS of 31% compared with low-disease burden (OS; 85%, EFS; 70%) and undetectable disease (OS; 95%, EFS; 72%; P < .0001 for OS and EFS). Grade ≥ 3 cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity rates were 21% and 7% overall and 35% and 9% in patients with HB, respectively.
Conclusion: Commercial tisagenlecleucel in CAYA RR B-ALL demonstrates efficacy and tolerability. This first analysis of commercial tisagenlecleucel stratified by disease burden identifies HB preinfusion to associate with inferior OS and EFS and increased toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures