PhosPiR: an automated phosphoproteomic pipeline in R
- PMID: 34882763
- PMCID: PMC8787428
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbab510
PhosPiR: an automated phosphoproteomic pipeline in R
Erratum in
-
Correction to: PhosPiR: an automated phosphoproteomic pipeline in R.Brief Bioinform. 2022 May 13;23(3):bbac153. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac153. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35393608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
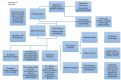
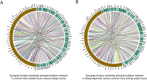
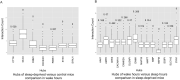
Large-scale phosphoproteome profiling using mass spectrometry (MS) provides functional insight that is crucial for disease biology and drug discovery. However, extracting biological understanding from these data is an arduous task requiring multiple analysis platforms that are not adapted for automated high-dimensional data analysis. Here, we introduce an integrated pipeline that combines several R packages to extract high-level biological understanding from large-scale phosphoproteomic data by seamless integration with existing databases and knowledge resources. In a single run, PhosPiR provides data clean-up, fast data overview, multiple statistical testing, differential expression analysis, phosphosite annotation and translation across species, multilevel enrichment analyses, proteome-wide kinase activity and substrate mapping and network hub analysis. Data output includes graphical formats such as heatmap, box-, volcano- and circos-plots. This resource is designed to assist proteome-wide data mining of pathophysiological mechanism without a need for programming knowledge.
Keywords: bioinformatics; data visualization; phosphoproteomics; pipeline; proteomics; statistics.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- Fischer EH. Cellular regulation by protein phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013;430:865–7. - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 2002;4:E127–30. - PubMed
-
- Jouy F, Müller SA, Wagner J, et al. Integration of conventional quantitative and phospho-proteomics reveals new elements in activated Jurkat T-cell receptor pathway maintenance. Proteomics 2015;15:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Francavilla C, Papetti M, Rigbolt KTG, et al. Multilayered proteomics reveals molecular switches dictating ligand-dependent EGFR trafficking. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2016;23:608–18. - PubMed
-
- Robles MS, Humphrey SJ, Mann M. Phosphorylation is a central mechanism for circadian control of metabolism and physiology. Cell Metab 2017;25:118–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

