The relative contributions of biomarkers, disease modifying treatment, and dementia severity to Alzheimer's stigma: A vignette-based experiment
- PMID: 34883313
- PMCID: PMC8748419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114620
The relative contributions of biomarkers, disease modifying treatment, and dementia severity to Alzheimer's stigma: A vignette-based experiment
Abstract
Objective: The symptoms and prognosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia contribute to the public's negative reactions toward individuals with AD dementia and their families. But what if, using AD biomarker tests, diagnosis was made before the onset of dementia, and a disease-modifying treatment was available? This study tests the hypotheses that a "preclinical" diagnosis of AD and treatment that improves prognosis will mitigate stigmatizing reactions.
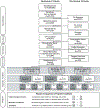
Methods: A sample of U.S. adults were randomized to receive one vignette created by a 3 × 2 × 2 vignette-based experiment that described a person with varied clinical symptom severity (Clinical Dementia Rating stages 0 (no dementia), 1 (mild), or 2 (moderate)), AD biomarker test results (positive vs negative), and disease-modifying treatment (available vs not available). Between-group comparisons were conducted of scores on the Modified Family Stigma in Alzheimer's Disease Scale (FS-ADS).
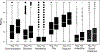
Results: The sample of 1,817 adults had a mean age two years younger than that of U.S. adults but was otherwise similar to the general adult population. The response rate was 63% and the completion rate was 96%. In comparisons of randomized groups, mild and moderate symptoms of dementia evoked stronger reactions on all FS-ADS domains compared to no dementia (all p < 0.001). A positive biomarker test result evoked stronger reactions on all but one FS-ADS domain (negative aesthetic attributions) compared to a negative biomarker result (all p < 0.001). Disease-modifying treatment had no measurable influence on stigma (all p > 0.05).
Conclusions: The stigmas of dementia spill over into preclinical AD, and availability of treatment does not alter that stigma. Translation of the preclinical AD construct from research into practice will require interventions that mitigate AD stigma to preserve the dignity and identity of individuals living with AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's biomarkers; Preclinical Alzheimer's; Stigma; Treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association National Plan Milestone Workgroup, Fargo KN, Aisen P, Albert M, Au R, Corrada MM, DeKosky S, Drachman D, Fillit H, Gitlin L, Haas M, Herrup K, Kawas C, Khachaturian AS, Khachaturian ZS, Klunk W, Knopman D, Kukull WA, Lamb B, Logsdon RG, Maruff P, Mesulam M, Mobley W, Mohs R, Morgan D, Nixon RA, Paul S, Petersen R, Plassman B, Potter W, Reiman E, Reisberg B, Sano M, Schindler R, Schneider LS, Snyder PJ, Sperling RA, Yaffe K, Bain LJ, Thies WH, Carrillo MC, 2014. 2014 Report on the Milestones for the US National Plan to Address Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement 10, S430–452. 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.08.103 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s vaccine shows promise in Phase II trial, n.d.. European Pharmaceutical Review. URL https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/156676/alzheimers-vacc... (accessed 10.29.21).
-
- American Community Survey (ACS) [WWW Document], n.d. The United States Census Bureau. URL https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs (accessed 4.28.20).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

