Lifestyle and Genetic Factors Modify Parent-of-Origin Effects on the Human Methylome
- PMID: 34883445
- PMCID: PMC8654798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103730
Lifestyle and Genetic Factors Modify Parent-of-Origin Effects on the Human Methylome
Abstract
Background: parent-of-origin effects (POE) play important roles in complex disease and thus understanding their regulation and associated molecular and phenotypic variation are warranted. Previous studies mainly focused on the detection of genomic regions or phenotypes regulated by POE. Understanding whether POE may be modified by environmental or genetic exposures is important for understanding of the source of POE-associated variation, but only a few case studies addressing modifiable POE exist.
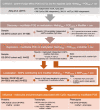
Methods: in order to understand this high order of POE regulation, we screened 101 genetic and environmental factors such as 'predicted mRNA expression levels' of DNA methylation/imprinting machinery genes and environmental exposures. POE-mQTL-modifier interaction models were proposed to test the potential of these factors to modify POE at DNA methylation using data from Generation Scotland: The Scottish Family Health Study(N=2315).
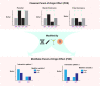
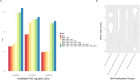
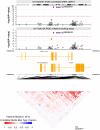
Findings: a set of vulnerable/modifiable POE-CpGs were identified (modifiable-POE-regulated CpGs, N=3). Four factors, 'lifetime smoking status' and 'predicted mRNA expression levels' of TET2, SIRT1 and KDM1A, were found to significantly modify the POE on the three CpGs in both discovery and replication datasets. We further identified plasma protein and health-related phenotypes associated with the methylation level of one of the identified CpGs.
Interpretation: the modifiable POE identified here revealed an important yet indirect path through which genetic background and environmental exposures introduce their effect on DNA methylation, motivating future comprehensive evaluation of the role of these modifiers in complex diseases.
Funding: NSFC (81971270),H2020-MSCA-ITN(721815), Wellcome (204979/Z/16/Z,104036/Z/14/Z), MRC (MC_UU_00007/10, MC_PC_U127592696), CSO (CZD/16/6,CZB/4/276, CZB/4/710), SFC (HR03006), EUROSPAN (LSHG-CT-2006-018947), BBSRC (BBS/E/D/30002276), SYSU, Arthritis Research UK, NHLBI, NIH.
Keywords: DNA methylation; DNA methylation machinery genes; interaction (modification) effect; mQTL; parent-of-origin effect; smoking.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. McIntosh reports grants from Janssen, grants from The Sackler Trust, personal fees from Illumina, personal fees from Janssen, during the conduct of the study; Dr. Haley reports grants from Medical Research Council, grants from Wellcome Trust, grants from Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates, grants from Scottish Funding Council, during the conduct of the study; Dr. Navarro reports grants from Medical Research Council, grants from Wellcome Trust, grants from Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorates, grants from Scottish Funding Council, during the conduct of the study. Dr. Bretherick reports grants from The Wellcome Trust, during the conduct of the study.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93020D00002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00007/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- 75N95020D00004/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 75N95020D00003/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N90020D00002/CL/CLC NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92022D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N96020D00002/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101921/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00003/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- 75N95020D00002/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL101250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N90020D00003/CL/CLC NIH HHS/United States
- 75N96020D00003/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00002/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00006/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 75N95020D00007/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- BB/I014144/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N95020D00005/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054474/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00005/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N98020D00007/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00004/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

