Past and Current Progress in the Development of Antiviral/Antimicrobial Polymer Coating towards COVID-19 Prevention: A Review
- PMID: 34883737
- PMCID: PMC8659939
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13234234
Past and Current Progress in the Development of Antiviral/Antimicrobial Polymer Coating towards COVID-19 Prevention: A Review
Abstract
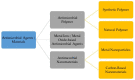
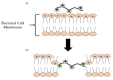
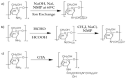
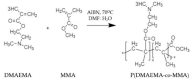
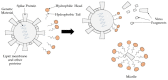
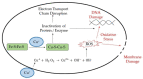
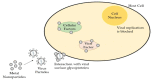
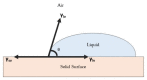
The astonishing outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, known as COVID-19, has attracted numerous research interests, particularly regarding fabricating antimicrobial surface coatings. This initiative is aimed at overcoming and minimizing viral and bacterial transmission to the human. When contaminated droplets from an infected individual land onto common surfaces, SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus is able to survive on various surfaces for up to 9 days. Thus, the possibility of virus transmission increases after touching or being in contact with contaminated surfaces. Herein, we aim to provide overviews of various types of antiviral and antimicrobial coating agents, such as antimicrobial polymer-based coating, metal-based coating, functional nanomaterial, and nanocomposite-based coating. The action mode for each type of antimicrobial agent against pathogens is elaborated. In addition, surface properties of the designed antiviral and antimicrobial polymer coating with their influencing factors are discussed in this review. This paper also exhibits several techniques on surface modification to improve surface properties. Various developed research on the development of antiviral/antimicrobial polymer coating to curb the COVID-19 pandemic are also presented in this review.
Keywords: COVID-19; antimicrobial; antiviral; coating; nanoparticles; polymer coating properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akuzov D., Franca L., Grunwald I., Vladkova T. Sharply reduced biofilm formation from Cobetia marina and in black sea water on modified siloxane coatings. Coatings. 2018;8:136. doi: 10.3390/coatings8040136. - DOI
-
- Zhang Z.P., Song X.F., Cui L.Y., Qi Y.H. Synthesis of polydimethylsiloxane-modified polyurethane and the structure and properties of its antifouling coatings. Coatings. 2018;8:157. doi: 10.3390/coatings8050157. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

