Level-K Classification from EEG Signals Using Transfer Learning
- PMID: 34883911
- PMCID: PMC8659931
- DOI: 10.3390/s21237908
Level-K Classification from EEG Signals Using Transfer Learning
Abstract
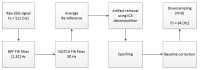
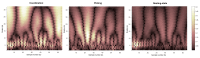
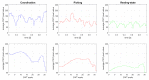
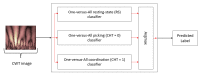
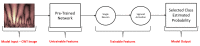
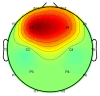
Tacit coordination games are games in which communication between the players is not allowed or not possible. In these games, the more salient solutions, that are often perceived as more prominent, are referred to as focal points. The level-k model states that players' decisions in tacit coordination games are a consequence of applying different decision rules at different depths of reasoning (level-k). A player at Lk=0 will randomly pick a solution, whereas a Lk≥1 player will apply their strategy based on their beliefs regarding the actions of the other players. The goal of this study was to examine, for the first time, the neural correlates of different reasoning levels in tacit coordination games. To that end, we have designed a combined behavioral-electrophysiological study with 3 different conditions, each resembling a different depth reasoning state: (1) resting state, (2) picking, and (3) coordination. By utilizing transfer learning and deep learning, we were able to achieve a precision of almost 100% (99.49%) for the resting-state condition, while for the picking and coordination conditions, the precision was 69.53% and 72.44%, respectively. The application of these findings and related future research options are discussed.
Keywords: EEG; classification; level-k; tacit coordination; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
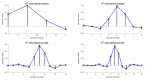
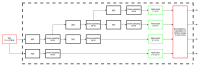
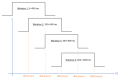
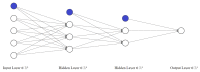


Similar articles
-
An Electrophysiological Model for Assessing Cognitive Load in Tacit Coordination Games.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 9;22(2):477. doi: 10.3390/s22020477. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062438 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Tacit Coordination Success Using Electroencephalogram Trajectories: The Impact of Task Difficulty.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;23(23):9493. doi: 10.3390/s23239493. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067866 Free PMC article.
-
Using a Stochastic Agent Model to Optimize Performance in Divergent Interest Tacit Coordination Games.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 8;20(24):7026. doi: 10.3390/s20247026. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33302476 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for electroencephalogram (EEG) classification tasks: a review.J Neural Eng. 2019 Jun;16(3):031001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab0ab5. Epub 2019 Feb 26. J Neural Eng. 2019. PMID: 30808014 Review.
-
A Review on Machine Learning for EEG Signal Processing in Bioengineering.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;14:204-218. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2020.2969915. Epub 2021 Jan 22. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 32011262 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling and predicting individual tacit coordination ability.Brain Inform. 2022 Feb 4;9(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40708-022-00152-w. Brain Inform. 2022. PMID: 35122193 Free PMC article.
-
An Electrophysiological Model for Assessing Cognitive Load in Tacit Coordination Games.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 9;22(2):477. doi: 10.3390/s22020477. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062438 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological Features to Aid in the Construction of Predictive Models of Human-Agent Collaboration in Smart Environments.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;22(17):6526. doi: 10.3390/s22176526. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080985 Free PMC article.
-
Offline EEG hyper-scanning using anonymous walk embeddings in tacit coordination games.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 20;18(7):e0288822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288822. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37471403 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Tacit Coordination Success Using Electroencephalogram Trajectories: The Impact of Task Difficulty.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;23(23):9493. doi: 10.3390/s23239493. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schelling T.C. The Strategy of Conflict. Harvard University Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1960.
-
- Zuckerman I., Kraus S., Rosenschein J.S. Using focal point learning to improve human-machine tacit coordination. Auton. Agents Multi. Agent Syst. 2011;22:289–316. doi: 10.1007/s10458-010-9126-5. - DOI
-
- Bacharach M., Stahl D.O. Variable-Frame Level-n Theory. Games Econ. Behav. 2000;32:220–246. doi: 10.1006/game.2000.0796. - DOI
-
- Bardsley N., Mehta J., Starmer C., Sugden R. Explaining Focal Points: Cognitive Hierarchy Theory versus Team Reasoning. Econ. J. 2009;120:40–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0297.2009.02304.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

