AI-Enabled Framework for Fog Computing Driven E-Healthcare Applications
- PMID: 34884048
- PMCID: PMC8659796
- DOI: 10.3390/s21238039
AI-Enabled Framework for Fog Computing Driven E-Healthcare Applications
Abstract
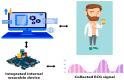
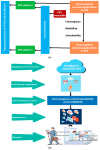
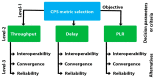
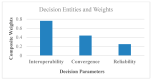
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the revolutionary paradigm to empower sixth generation (6G) edge computing based e-healthcare for everyone. Thus, this research aims to promote an AI-based cost-effective and efficient healthcare application. The cyber physical system (CPS) is a key player in the internet world where humans and their personal devices such as cell phones, laptops, wearables, etc., facilitate the healthcare environment. The data extracting, examining and monitoring strategies from sensors and actuators in the entire medical landscape are facilitated by cloud-enabled technologies for absorbing and accepting the entire emerging wave of revolution. The efficient and accurate examination of voluminous data from the sensor devices poses restrictions in terms of bandwidth, delay and energy. Due to the heterogeneous nature of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), the driven healthcare system must be smart, interoperable, convergent, and reliable to provide pervasive and cost-effective healthcare platforms. Unfortunately, because of higher power consumption and lesser packet delivery rate, achieving interoperable, convergent, and reliable transmission is challenging in connected healthcare. In such a scenario, this paper has fourfold major contributions. The first contribution is the development of a single chip wearable electrocardiogram (ECG) with the support of an analog front end (AFE) chip model (i.e., ADS1292R) for gathering the ECG data to examine the health status of elderly or chronic patients with the IoT-based cyber physical system (CPS). The second proposes a fuzzy-based sustainable, interoperable, and reliable algorithm (FSIRA), which is an intelligent and self-adaptive decision-making approach to prioritize emergency and critical patients in association with the selected parameters for improving healthcare quality at reasonable costs. The third is the proposal of a specific cloud-based architecture for mobile and connected healthcare. The fourth is the identification of the right balance between reliability, packet loss ratio, convergence, latency, interoperability, and throughput to support an adaptive IoMT driven connected healthcare. It is examined and observed that our proposed approaches outperform the conventional techniques by providing high reliability, high convergence, interoperability, and a better foundation to analyze and interpret the accuracy in systems from a medical health aspect. As for the IoMT, an enabled healthcare cloud is the key ingredient on which to focus, as it also faces the big hurdle of less bandwidth, more delay and energy drain. Thus, we propose the mathematical trade-offs between bandwidth, interoperability, reliability, delay, and energy dissipation for IoMT-oriented smart healthcare over a 6G platform.
Keywords: 6G; AI; analytic hierarchy process; cyber physical system; e-health; fog computing; interoperability.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between all authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
AI-driven adaptive reliable and sustainable approach for internet of things enabled healthcare system.Math Biosci Eng. 2022 Feb 11;19(4):3953-3971. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022182. Math Biosci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35341282
-
Remote Pain Monitoring Using Fog Computing for e-Healthcare: An Efficient Architecture.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 18;20(22):6574. doi: 10.3390/s20226574. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33217896 Free PMC article.
-
Secure Smart Wearable Computing through Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems for Health Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;22(3):1076. doi: 10.3390/s22031076. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161820 Free PMC article.
-
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)-Based Smart Healthcare System: Trends and Progress.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 16;2022:7218113. doi: 10.1155/2022/7218113. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9768292. doi: 10.1155/2023/9768292. PMID: 35880061 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;12(8):562. doi: 10.3390/bios12080562. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Feasibility of a Novel Clinical Decision Support System Based on the Automatic Generation of Alerts through Remote Patient Monitoring.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 8;13(19):5974. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195974. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39408035 Free PMC article.
-
Empowering People with Disabilities in Smart Homes Using Predictive Informing.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 6;25(1):284. doi: 10.3390/s25010284. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39797073 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of Claude 3.5-Sonnet and human physicians in generating discharge summaries for patients with renal insufficiency: assessment of efficiency, accuracy, and quality.Front Digit Health. 2024 Dec 5;6:1456911. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1456911. eCollection 2024. Front Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39703756 Free PMC article.
-
A Proof-of-Concept IoT System for Remote Healthcare Based on Interoperability Standards.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;22(4):1646. doi: 10.3390/s22041646. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214548 Free PMC article.
-
Textile-Based Flexible Capacitive Pressure Sensors: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;12(9):1495. doi: 10.3390/nano12091495. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35564203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sabuzima N., Ripon P. 6G communication technology: A vision on intelligent healthcare. IEEE IoT J. 2020;7:1–9.
-
- Padhi P.K., Charrua-Santos F. 6G enabled tactile internet and cognitive internet of healthcare everything: Towards a theoretical framework. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021;4:66. doi: 10.3390/asi4030066. - DOI
-
- Sodhro A.H., Pirbhulal S., Muhammad K. Towards 6G architecture for energy efficient communication in IoT-enabled smart automation systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021;8:5141–5146. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3024715. - DOI
-
- Zhang L., Liang Y.-C., Niyato D. 6G visions: Mobile ultra-broadband, super IoT, and AI. China Commun. 2019;16:1–14.
-
- Zong B., Fan C., Wang X., Duan X., Wang B., Wang J. 6G technologies: Key drivers, core requirements, system architectures, and enabling technologies. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019;14:18–27. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2921398. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

