Large-Scale Internet of Things Multi-Sensor Measurement Node for Smart Grid Enhancement
- PMID: 34884097
- PMCID: PMC8662425
- DOI: 10.3390/s21238093
Large-Scale Internet of Things Multi-Sensor Measurement Node for Smart Grid Enhancement
Abstract
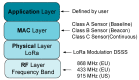
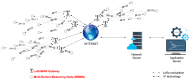
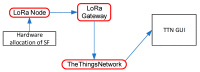
Electric power infrastructure has revolutionized our world and our way of living has completely changed. The necessary amount of energy is increasing faster than we realize. In these conditions, the grid is forced to run against its limitations, resulting in more frequent blackouts. Thus, urgent solutions need to be found to meet this greater and greater energy demand. By using the internet of things infrastructure, we can remotely manage distribution points, receiving data that can predict any future failure points on the grid. In this work, we present the design of a fully reconfigurable wireless sensor node that can sense the smart grid environment. The proposed prototype uses a modular developed hardware platform that can be easily integrated into the smart grid concept in a scalable manner and collects data using the LoRaWAN communication protocol. The designed architecture was tested for a period of 6 months, revealing the feasibility and scalability of the system, and opening new directions in the remote failure prediction of low voltage/medium voltage switchgears on the electric grid.
Keywords: LoRaWAN; partial discharge; predictive maintenance; scalability; smart grid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Fu G., Wilkinson S., Dawson R.J., Fowler H.J., Kilsby C., Panteli M., Mancarella P. Integrated Approach to Assess the Resilience of Future Electricity Infrastructure Networks to Climate Hazards. IEEE Syst. J. 2018;12:3169–3180. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2700791. - DOI
-
- Morello R., Capua C., Fulco G., Mukhopadhyay S.C. A Smart Power Meter to Monitor Energy Flow in Smart Grids: The Role of Advanced Sensing and IoT in the Electric Grid of the Future. IEEE Sens. J. 2017;17:7828–7837. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2760014. - DOI
-
- Raboaca M.S., Meheden M., Musat A., Viziteu A., Creanga A., Vlad V., Filote C., Rata M., Lavric A. An overview and performance evaluation of open charge point protocol from an electromobility concept perspective. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021:1–21. doi: 10.1002/er.7206. - DOI
-
- Bansal P., Singh A. Smart metering in Smart Grid Framework: A Review; Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC); Waknaghat, India. 22–24 December 2016.
-
- Ma J., Zheng Y., Ning H., Yang L.T., Huang R., Liu H., Mu Q., Yau S.S. Top Challenges for Smart Worlds: A Report on the Top10Cs Forum. IEEE Access. 2015;3:2475–2480. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2504123. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

