Psychological Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Out-of-Hospital Health Professionals: A Living Systematic Review
- PMID: 34884280
- PMCID: PMC8658089
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10235578
Psychological Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Out-of-Hospital Health Professionals: A Living Systematic Review
Abstract
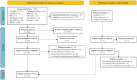
Health professionals (HPs), especially those working in the front line, have been one of the groups most affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. The objective of this study is to identify the best available scientific evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of out-of-hospital HPs in terms of stress, anxiety, depression, and self-efficacy. A living systematic review of the literature was designed, consulting the electronic online versions of the CINHAL, Cochrane Library, Cuiden, IBECS, JBI, LILACS, Medline PyscoDoc, PsycoINFO, Scopus, and Web of Science databases in November 2021. Original research was selected, published in either English, Spanish, French, Italian, or Portuguese. In total, 2082 publications were identified, of which 16 were included in this review. The mental health of out-of-hospital HPs was affected. Being a woman or having direct contact with patients showing suspicious signs of COVID-19 or confirmed cases were the factors related to a greater risk of developing high levels of stress and anxiety; in the case of depressive symptoms, it was having a clinical history of illnesses that could weaken their defenses against infection. Stopping unpleasant emotions and thoughts was the coping strategy most frequently used by these HPs.
Keywords: COVID-19; anxiety; depression; health professionals; mental health; out-of-hospital; pandemic; self-efficacy; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization(WHO) Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) [(accessed on 29 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting...
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

