Focal Point of Fanconi Anemia Signaling
- PMID: 34884777
- PMCID: PMC8657418
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222312976
Focal Point of Fanconi Anemia Signaling
Abstract
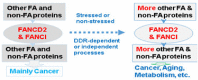
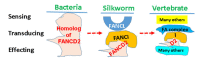
Among human genetic diseases, Fanconi Anemia (FA) tops all with its largest number of health complications in nearly all human organ systems, suggesting the significant roles played by FA genes in the maintenance of human health. With the accumulated research on FA, the encoded protein products by FA genes have been building up to the biggest cell defense signaling network, composed of not only 22+ FA proteins but also ATM, ATR, and many other non-FA proteins. The FA D2 group protein (FANCD2) and its paralog form the focal point of FA signaling to converge the effects of its upstream players in response to a variety of cellular insults and simultaneously with downstream players to protect humans from contracting diseases, including aging and cancer. In this review, we update and discuss how the FA signaling crucially eases cellular stresses through understanding its focal point.
Keywords: DNA damage response; fanconi anemia; genetic disease; genome stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bhandari J., Thada P.K., Puckett Y. StatPearls. NCBI Bookshelf; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2021. Fanconi Anemia.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

