UMPred-FRL: A New Approach for Accurate Prediction of Umami Peptides Using Feature Representation Learning
- PMID: 34884927
- PMCID: PMC8658322
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222313124
UMPred-FRL: A New Approach for Accurate Prediction of Umami Peptides Using Feature Representation Learning
Abstract
Umami ingredients have been identified as important factors in food seasoning and production. Traditional experimental methods for characterizing peptides exhibiting umami sensory properties (umami peptides) are time-consuming, laborious, and costly. As a result, it is preferable to develop computational tools for the large-scale identification of available sequences in order to identify novel peptides with umami sensory properties. Although a computational tool has been developed for this purpose, its predictive performance is still insufficient. In this study, we use a feature representation learning approach to create a novel machine-learning meta-predictor called UMPred-FRL for improved umami peptide identification. We combined six well-known machine learning algorithms (extremely randomized trees, k-nearest neighbor, logistic regression, partial least squares, random forest, and support vector machine) with seven different feature encodings (amino acid composition, amphiphilic pseudo-amino acid composition, dipeptide composition, composition-transition-distribution, and pseudo-amino acid composition) to develop the final meta-predictor. Extensive experimental results demonstrated that UMPred-FRL was effective and achieved more accurate performance on the benchmark dataset compared to its baseline models, and consistently outperformed the existing method on the independent test dataset. Finally, to aid in the high-throughput identification of umami peptides, the UMPred-FRL web server was established and made freely available online. It is expected that UMPred-FRL will be a powerful tool for the cost-effective large-scale screening of candidate peptides with potential umami sensory properties.
Keywords: bioinformatics; feature representation learning; machine learning; sequence analysis; umami peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
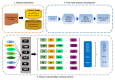
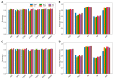
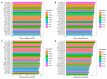
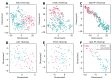
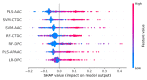
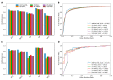
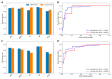
References
-
- Dang Y., Gao X., Ma F., Wu X. Comparison of umami taste peptides in water-soluble extractions of Jinhua and Parma hams. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015;60:1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.014. - DOI
-
- Wang W., Zhou X., Liu Y. Characterization and evaluation of umami taste: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;127:115876. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.115876. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

