Prediction of Prostate Cancer Disease Aggressiveness Using Bi-Parametric Mri Radiomics
- PMID: 34885175
- PMCID: PMC8657292
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13236065
Prediction of Prostate Cancer Disease Aggressiveness Using Bi-Parametric Mri Radiomics
Abstract
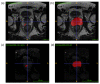
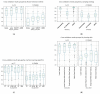
Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers in the male population. Its diagnosis and classification rely on unspecific measures such as PSA levels and DRE, followed by biopsy, where an aggressiveness level is assigned in the form of Gleason Score. Efforts have been made in the past to use radiomics coupled with machine learning to predict prostate cancer aggressiveness from clinical images, showing promising results. Thus, the main goal of this work was to develop supervised machine learning models exploiting radiomic features extracted from bpMRI examinations, to predict biological aggressiveness; 288 classifiers were developed, corresponding to different combinations of pipeline aspects, namely, type of input data, sampling strategy, feature selection method and machine learning algorithm. On a cohort of 281 lesions from 183 patients, it was found that (1) radiomic features extracted from the lesion volume of interest were less stable to segmentation than the equivalent extraction from the whole gland volume of interest; and (2) radiomic features extracted from the whole gland volume of interest produced higher performance and less overfitted classifiers than radiomic features extracted from the lesions volumes of interest. This result suggests that the areas surrounding the tumour lesions offer relevant information regarding the Gleason Score that is ultimately attributed to that lesion.
Keywords: bi-parametric MRI; machine learning; prostate cancer; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, The Global Cancer Observatory World Fact-Sheet. [(accessed on 1 March 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers.
-
- Catalona W.J., Richie J.P., Ahmann F.R., Hudson M.A., Scardino P.T., Flanigan R.C., Dekernion J.B., Ratliff T.L., Kavoussi L.R., Dalkin B.L., et al. Comparison of digital rectal examination and serum prostate specific antigen in the early detection of prostate cancer: Results of a multicenter clinical trial of 6630 men. J. Urol. 1994;151:1283–1290. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)35233-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Halpern J.A., Oromendia C., Shoag J.E., Mittal S., Cosiano M.F., Ballman K.V., Vickers A.J., Hu J.C. Use of digital rectal examination as an adjunct to prostate specific antigen in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2018;199:947–953. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.10.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

