Effect of Edible Onion (Allium cepa L.) Film on Quality, Sensory Properties and Shelf Life of Beef Burger Patties
- PMID: 34885783
- PMCID: PMC8659084
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26237202
Effect of Edible Onion (Allium cepa L.) Film on Quality, Sensory Properties and Shelf Life of Beef Burger Patties
Abstract
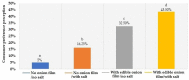
The production of edible film from onion (Allium cepa L.) to be applied as packaging is attractive, due to its chemical properties and biodegradable characteristics. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that edible onion film can positively influence the sensory properties, quality and increasing shelf life of beef burgers patties. The experiment was designed in a 4 × 2 factorial scheme, with two treatments (beef burgers patties with or without edible onion film) at an interval of four storage times (0, 3, 6 and 9 days) at 4 °C. The uncoated burger patties (control) suffered the most intense color modifications during the storage (p < 0.05). The luminosity index was higher (p < 0.05) in the control at all storage times, except at day 6, and redness, yellowness and chrome were higher (p < 0.05) in the edible onion film patties at all storage times. The pH of the beef burger patties was lower (p < 0.05) at all storage times when the edible onion film was applied. For the texture profile, only the chewiness was affected, as the inclusion of the edible onion film improved the chewing of the beef burgers patties over the storage time (p < 0.05). Additionally, there was an inhibition of the microbial growth of mesophiles and psychrophiles with the application of the edible onion film in beef burgers patties. The use of edible onion film improved the perception of panelists for the variables texture, color, flavor, odor and overall appearance, and increased the preference of panelists. The edible onion film is recommended for preserving beef burgers patties, as it delays the proliferation of unwanted microorganisms, stabilizes and improves the color parameters and sensory attributes, and increases the overall acceptance of the consumer.
Keywords: antimicrobial; beef burgers patties; edible coating; lipid oxidation; texture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that there are no conflict of interest of any kind that could have appeared to affect the reported work in this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Characterization of κ-Carrageenan-Based Edible Films Enriched With Resveratrol or Quercetin for Shelf-Life Extension of Goat Meat Burger Patties.J Food Sci. 2025 May;90(5):e70277. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70277. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40387509 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of onion skin powder on color, lipid, and protein oxidative stability of premade beef patty during cold storage.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 6;14(1):20816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71265-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39242593 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of clove extract on oxidative stability and sensory attributes in cooked beef patties at refrigerated storage.Meat Sci. 2020 Mar;161:107972. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.107972. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Meat Sci. 2020. PMID: 31675647
-
Onion (Allium cepa L.) peel: A review on the extraction of bioactive compounds, its antioxidant potential, and its application as a functional food ingredient.J Food Sci. 2022 Oct;87(10):4289-4311. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16297. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36101019 Review.
-
Edible Film Casting Techniques and Materials and Their Utilization for Meat-Based Product Packaging.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jun 24;15(13):2800. doi: 10.3390/polym15132800. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Self-Supported Biopolymeric Films Based on Onion Bulb (Allium cepa L.): Gamma-Radiation Effects in Sterilizing Doses.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 11;15(4):914. doi: 10.3390/polym15040914. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850198 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Beef Burgers Formulated with Fat Substitute in a Form of Freeze-Dried Hydrogel Enriched with Açai Oil.Molecules. 2022 Jun 9;27(12):3700. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123700. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744826 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Chlorella vulgaris Fortification on the Nutritional Composition and Quality Characteristics of Beef Burgers.Foods. 2024 Jun 20;13(12):1945. doi: 10.3390/foods13121945. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928886 Free PMC article.
-
Laponite®-From Dispersion to Gel-Structure, Properties, and Applications.Molecules. 2024 Jun 13;29(12):2823. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122823. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation the Potential of Onion/Laponite Composites Films for Sustainable Food Packaging with Enhanced UV Protection and Antioxidant Capacity.Molecules. 2023 Sep 27;28(19):6829. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196829. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar Y., Yadav D.N., Ahmad T., Narsaiah K. Recent Trends in the Use of Natural Antioxidants for Meat and Meat Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015;14:796–812. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12156. - DOI
-
- Vasconcelos L., de Souza M., de Oliveira J., Silva Filho E., Silva A., Mazzetto S.E., Pereira E.S., Oliveira R.L., Bezerra L. Elaboration and Characterization of Bioactive Films Obtained from the Incorporation of Cashew Nut Shell Liquid into a Matrix of Sodium Alginate. Antioxidants. 2021;10:1378. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

