Natural Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor 5- O-Caffeoylshikimic Acid Ameliorates Kidney Injury Caused by Hyperuricemia in Mice
- PMID: 34885887
- PMCID: PMC8659034
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26237307
Natural Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor 5- O-Caffeoylshikimic Acid Ameliorates Kidney Injury Caused by Hyperuricemia in Mice
Abstract
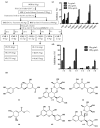
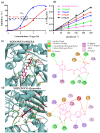
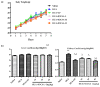
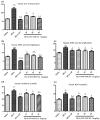
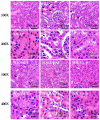
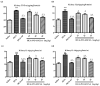
Xanthine oxidase (XOD) inhibition has long been considered an effective anti-hyperuricemia strategy. To identify effective natural XOD inhibitors with little side effects, we performed a XOD inhibitory assay-coupled isolation of compounds from Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma (SGR), a traditional Chinese medicine frequently prescribed as anti-hyperuricemia agent for centuries. Through the in vitro XOD inhibitory assay, we obtained a novel XOD inhibitor, 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid (#1, 5OCSA) with IC50 of 13.96 μM, as well as two known XOD inhibitors, quercetin (#3) and astilbin (#6). Meanwhile, we performed in silico molecular docking and found 5OCSA could interact with the active sites of XOD (PDB ID: 3NVY) with a binding energy of -8.6 kcal/mol, suggesting 5OCSA inhibits XOD by binding with its active site. To evaluate the in vivo effects on XOD, we generated a hyperuricemia mice model by intraperitoneal injection of potassium oxonate (300 mg/kg) and oral gavage of hypoxanthine (500 mg/kg) for 7 days. 5OCSA could inhibit both hepatic and serum XOD in vivo, together with an improvement of histological and multiple serological parameters in kidney injury and HUA. Collectively, our results suggested that 5OCSA may be developed into a safe and effective XOD inhibitor based on in vitro, in silico and in vivo evidence.
Keywords: 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid; Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma; XOD inhibitor; hyperuricemia; potassium oxonate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isorhamnetin, the xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Sophora japonica, ameliorates uric acid levels and renal function in hyperuricemic mice.Food Funct. 2021 Dec 13;12(24):12503-12512. doi: 10.1039/d1fo02719k. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34806108
-
4-(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)amino)ethyl)benzene-1, 3-diol is a potential agent for gout therapy as a dual inhibitor of XOD and NLRP3.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;42:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.007. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29655702
-
Protective effects of Rhizoma smilacis glabrae extracts on potassium oxonate- and monosodium urate-induced hyperuricemia and gout in mice.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jun;59:152772. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.032. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31005813
-
Natural compounds with xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity: A review.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019 Apr;93(4):387-418. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13437. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019. PMID: 30403440 Review.
-
Advances in the chemical constituents, pharmacological activity, and clinical application of Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma: A review and predictive analysis of quality markers (Q-markers).Heliyon. 2024 Apr 12;10(8):e29557. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29557. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wuling San Based on Network Pharmacology and in vivo Evidence Against Hyperuricemia via Improving Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting Inflammation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Mar 4;17:675-690. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S398625. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36911073 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-hyperuricemia potential of bioactive natural products and extracts derived from traditional Chinese medicines: A review and perspective.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Jul;15(7):101183. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101183. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40708571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Qinpi Tongfeng Formula in the Treatment of Acute Gouty Arthritis: A Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 12;2022:7873426. doi: 10.1155/2022/7873426. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35865342 Free PMC article.
-
Shikimic acid recovers diarrhea and its complications in SD rats fed lactose diet to induce diarrhea.Lab Anim Res. 2023 Nov 10;39(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s42826-023-00179-y. Lab Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 37950334 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-hyperuricemia effect of Clerodendranthus spicatus: a molecular biology study combined with metabolomics.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):15449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66454-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38965392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu S. Danxi Xinfa and Zhu Danxi’s correlated works. Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi. 1995;25:111–113. - PubMed
-
- Arersa K.K., Wondimnew T., Welde M., Husen T.M. Prevalence and Determinants of Hyperuricemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Attending Jimma Medical Center, Southwestern Ethiopia, 2019. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020;13:2059–2067. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S252825. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

