Development of a Continuous System for 2-Phenylethanol Bioproduction by Yeast on Whey Permeate-Based Medium
- PMID: 34885969
- PMCID: PMC8658864
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26237388
Development of a Continuous System for 2-Phenylethanol Bioproduction by Yeast on Whey Permeate-Based Medium
Abstract
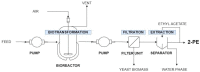
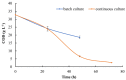
2-Phenylethanol (2-PE) is an alcohol with a rosy scent and antimicrobial activity, and therefore, it is widely used in the food and cosmetic industries as an aroma and preservative. This work was aimed to draw up a technology for 2-PE bioproduction on whey permeate, which is waste produced by the dairy industry, rich in lactase and proteins. Its composition makes it a harmful waste to dispose of; however, with a properly selected microorganism, it could be converted to a value-added product. Herein, two yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus strains and one Kluyveromyces lactis, isolated from dairy products, were tested for 2-PE production, firstly on standard media and then on whey permeate based media in batch cultures. Thereafter, the 2-PE bioproduction in a continuous system in a 4.8 L bioreactor was developed, and subsequently, the final product was recovered from culture broth. The results showed that the yield of 2-PE production increased by 60% in the continuous culture compared to batch culture. Together with a notable reduction of chemical oxygen demand for whey permeate, the present study reports a complete, effective, and environmentally friendly strategy for 2-PE bioproduction with a space-time yield of 57.5 mg L-1 h-1.
Keywords: 2-phenylethanol; Kluyveromyces; batch culture; bioreactor; continuous culture; whey permeate; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Valorisation of Whey Permeate in Sequential Bioprocesses towards Value-Added Products-Optimisation of Biphasic and Classical Batch Cultures of Kluyveromyces marxianus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 20;24(8):7560. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087560. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108722 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological 2-Phenylethanol Production: Recent Developments.Molecules. 2024 Dec 5;29(23):5761. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235761. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of yeasts for the production of 2-phenylethanol (rose aroma) in organic waste-based media.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018 Feb;66(2):153-160. doi: 10.1111/lam.12835. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29224193
-
Fed-Batch and Sequential-Batch Approaches To Enhance the Bioproduction of 2-Phenylethanol and 2-Phenethyl Acetate in Solid-State Fermentation Residue-Based Systems.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Mar 27;67(12):3389-3399. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00524. Epub 2019 Mar 7. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30816043
-
Production of bioingredients from Kluyveromyces marxianus grown on whey: an alternative.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1998 Oct;38(7):565-98. doi: 10.1080/10408699891274318. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1998. PMID: 9813735 Review.
Cited by
-
Rosenbergiella meliponini D21B Isolated from Pollen Pots of the Australian Stingless Bee Tetragonula carbonaria.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 12;11(4):1005. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11041005. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37110428 Free PMC article.
-
Valorisation of Whey Permeate in Sequential Bioprocesses towards Value-Added Products-Optimisation of Biphasic and Classical Batch Cultures of Kluyveromyces marxianus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 20;24(8):7560. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087560. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108722 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological 2-Phenylethanol Production: Recent Developments.Molecules. 2024 Dec 5;29(23):5761. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235761. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uçkun Kiran E., Trzcinski A.P., Ng W.J., Liu Y. Enzyme Production from Food Wastes Using a Biorefinery Concept. Waste and Biomass Valorization. 2014;5:903–917. doi: 10.1007/s12649-014-9311-x. - DOI
-
- Das M., Raychaudhuri A., Ghosh S.K. Supply Chain of Bioethanol Production from Whey: A Review. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016;35:833–846. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.100. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

