Increased Work from Home and Low Back Pain among Japanese Desk Workers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 34886088
- PMCID: PMC8657068
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182312363
Increased Work from Home and Low Back Pain among Japanese Desk Workers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
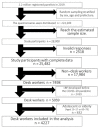
To prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), desk workers in Japan have been encouraged to work from home. Due to rapidly increased working from home, working in environments that are not properly designed and working with poor posture can affect low back pain (LBP). This study aimed to examine the relationship between increased work from home during the COVID-19 pandemic and LBP among Japanese desk workers. Using study data from the Japan COVID-19 and Society Internet Survey 2020 conducted from August to September 2020, 4227 desk workers who did not have LBP before the COVID-19 pandemic were analyzed out of 25,482 total respondents. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for LBP were calculated by multivariable logistic regression, adjusting for covariates such as socioeconomic factors. During the COVID-19 pandemic, 31.3% of desk workers with an increased chance of working from home, and 4.1% had LBP. Desk workers with increased working from home were more likely to have LBP (OR: 2.00 (95% CI, 1.36-2.93)). In this large-scale study, increased work from home was associated with LBP among desk workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, preparing an appropriate work environment for desk workers working from home can improve productivity, leading to positive effects.
Keywords: COVID-19; Internet survey; Japan; cross-sectional study; desk worker; low back pain; work from home.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- Ministry of Health LaW . The Number of People Tested Positive for COVID-19 Number of PCR Tests (From 15 January 2020 to 6 April 2020) Ministry of Health LaW; Tokyo, Japan: 2020.
-
- Goto M. Trends in Surveys about Home Teleworking during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Japan. J. Inst. Nucl. Saf. Syst. 2020;27:252–274.
-
- Park S.M., Kim H.J., Jeong H., Kim H., Chang B.S., Lee C.K., Yeom J.S. Longer sitting time and low physical activity are closely associated with chronic low back pain in population over 50 years of age: A cross-sectional study using the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Spine J. Off. J. N. Am. Spine Soc. 2018;18:2051–2058. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 17H03589, 19K10671, 19K10446, 18H03107, and 18H03062/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 19FA1005 and 19FG2001/the Research Support Program to Apply the Wisdom of the University to Tackle COVID-19 Re-lated Emergency Problems, University of Tsukuba, and Health Labour Sciences Research grants
- 19K19439/JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous